Forest recovering from Mt. St. Helens explosion: research (w/ Video)
(Phys.org) -- Mt. St. Helens exploded 32 years ago on May 18. It began with a small series of earthquakes and culminated with the volcano erupting, a cataclysmic collapse of the flank of the mountain and the largest landslide in recorded history.
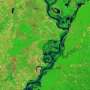
This time series of data shows the explosion and subsequent recovery of life on the volcano. Landsat, a satellite program operated by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey acquired the images between 1979 and 2011. In them, scientists have an unprecedented opportunity to witness how life recovers from devastation.
The animation begins with vegetation as red because early Landsat satellites couldn't 'see' blue light. That changed with launch of Landsat 5 in 1984 and its natural color abilities.
The collapse of the mountain was like uncorking a bottle of champagne. Fifty-seven people died when rocks, hot ash, gas and steam exploded out of the Earth. The blast debris, which is gray in the images, covered over 230 square miles (600 square kilometers) and blew down 4 billion board-feet of timber.
The landslide buried 14 miles (23 kilometers) of the North Fork Toutle River with an average of 150 feet (46 meters) of rocks, dirt and uprooted trees. In some places the debris was as deep as 600 feet (180 meters) high.
The squarish beige patches visible in the upper right and lower left of the animation show logging on the mountain both before and after the eruption.
This image was created using the reflected light from the near infrared, green and red portions of the spectrum from instruments aboard Landsat satellites 2 and 3 and from the blue, green and red portions of the spectrum from instruments aboard Landsat satellites 5 and 7.
Landsat 2 launched in 1975 and provided scientific data for 7 years until 1982. Landsat 3 launched in 1978 and ran for 5 years until1983. NASA launched Landsat 5 in 1984 and it ran for a record-breaking 28 years. Landsat 7 is still up and running; it was launched in 1999. The data from these and other Landsat satellites has been instrumental in our understanding of forest health, storm damage, agricultural trends, urban growth and many other ongoing changes to our land.
NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available data over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013.
Provided by JPL/NASA