Discovery of the Musket Ball Cluster

(Phys.org) -- Using a combination of powerful observatories in space and on the ground, astronomers have observed a violent collision between two galaxy clusters in which so-called normal matter has been wrenched apart from dark matter through a violent collision between two galaxy clusters.
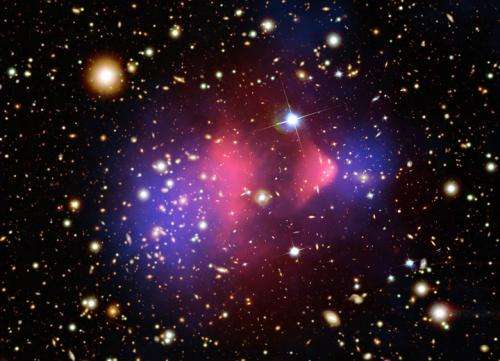
The newly discovered galaxy cluster is called DLSCL J0916.2+2951. It is similar to the Bullet Cluster, the first system in which the separation of dark and normal matter was observed, but with some important differences. The newly discovered system has been nicknamed the "Musket Ball Cluster" because the cluster collision is older and slower than the Bullet Cluster.
Finding another system that is further along in its evolution than the Bullet Cluster gives scientists valuable insight into a different phase of how galaxy clusters - the largest known objects held together by gravity - grow and change after major collisions. Researchers used observations from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope as well as the Keck, Subaru and Kitt Peak Mayall telescopes to show that hot, X-ray bright gas in the Musket Ball Cluster has been clearly separated from dark matter and galaxies.
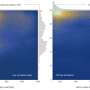
In this composite image, the hot gas observed with Chandra is colored red, and the galaxies in the optical image from Hubble appear as mostly white and yellow. The location of the majority of the matter in the cluster (dominated by dark matter) is colored blue. When the red and the blue regions overlap, the result is purple as seen in the image. The matter distribution is determined by using data from Subaru, Hubble and the Mayall telescope that reveal the effects of gravitational lensing, an effect predicted by Einstein where large masses can distort the light from distant objects.
In addition to the Bullet Cluster, five other similar examples of merging clusters with separation between normal and dark matter and varying levels of complexity, have previously been found. In these six systems, the collision is estimated to have occurred between 170 million and 250 million years earlier.
In the Musket Ball Cluster, the system is observed about 700 million years after the collision. Taking into account the uncertainties in the age estimate, the merger that has formed the Musket Ball Cluster is two to five times further along than in previously observed systems. Also, the relative speed of the two clusters that collided to form the Musket Ball cluster was lower than most of the other Bullet Cluster-like objects.
The special environment of galaxy clusters, including the effects of frequent collisions with other clusters or groups of galaxies and the presence of large amounts of hot, intergalactic gas, is likely to play an important role in the evolution of their member galaxies. However, it is still unclear whether cluster mergers trigger star formation, suppress it, or have little immediate effect. The Musket Ball Cluster holds promise for deciding between these alternatives.
The Musket Ball Cluster also allows an independent study of whether dark matter can interact with itself. This information is important for narrowing down the type of particle that may be responsible for dark matter. No evidence is reported for self-interaction in the Musket Ball Cluster, consistent with the results for the Bullet Cluster and the other similar clusters.
The Musket Ball Cluster is located about 5.2 billion light years away from Earth. Findings on the Musket Ball Cluster were presented at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Austin, TX in January by Will Dawson from the University of California, Davis.
More information: A paper describing these results led by Dawson was published in the March 10, 2012 issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Provided by Chandra X-ray Center