China launches rocket carrying new constellation of satellites
China says it launched a rocket Tuesday carrying a constellation of a reported 18 satellites as part of efforts to assert its presence in space.

China says it launched a rocket Tuesday carrying a constellation of a reported 18 satellites as part of efforts to assert its presence in space.
Space Exploration
15 hours ago
0
5

Medications used by astronauts on the International Space Station might not be good enough for a three-year journey to Mars. A new study led by Duke Health shows that over half of the medicines stocked in space—staples ...
Space Exploration
Jul 23, 2024
1
95

Scientists from RMIT University have led a world-first study on common food aromas that may help explain why astronauts report that meals taste bland in space and struggle to eat their normal nutritional intake.
Space Exploration
Jul 16, 2024
0
9
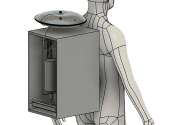
Astronauts on spacewalks famously have to relieve themselves inside their spacesuits. Not only is this uncomfortable for the wearer and unhygienic, it is also wasteful, as—unlike wastewater on board the International Space ...
Space Exploration
Jul 12, 2024
0
65

Two astronauts who should have been back on Earth weeks ago said Wednesday that they're confident that Boeing's space capsule can return them safely, despite a string of vexing breakdowns.
Space Exploration
Jul 10, 2024
0
2

Technicians lift NASA's Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell on June 28, 2024. The integrated spacecraft, which will be used for the Artemis II mission to orbit the moon, has been undergoing ...
Space Exploration
Jul 3, 2024
0
4

Robotic companions are a mainstay of sci-fi series everywhere. From R2D2 to Johnny 5, these characters typically have a supporting role in the story and are helpful to their human companions. But what if they were integral ...
Space Exploration
Jul 2, 2024
0
38

NASA on Monday canceled a spacewalk at the International Space Station after water leaked from an astronaut's spacesuit.
Space Exploration
Jun 25, 2024
0
9

How bad for your health is space travel? Answering this question will be crucial not just for astronauts aiming to go to Mars, but for a booming space tourism industry planning to blast anyone who can afford it into orbit.
Space Exploration
Jun 11, 2024
1
64

After years of stumbles and delays, Boeing has finally launched astronauts to the International Space Station for NASA.
Space Exploration
Jun 5, 2024
0
1
Astronautics, and related astronautical engineering, is the theory and practice of navigation beyond the Earth's atmosphere. In other words, it is the science and technology of space flight.
The term astronautics was coined by analogy with aeronautics. As there is a certain degree of technology overlapping between the two fields, the term aerospace is often used to describe them both.
As with aeronautics, the restrictions of mass, temperatures, and external forces require that applications in space survive extreme conditions: high-grade vacuum, the radiation bombardment of interplanetary space, the magnetic belts of low Earth orbit. Space launch vehicles must withstand titanic forces, while satellites can experience huge variations in temperature in very brief periods. Extreme constraints on mass cause astronautical engineers to face the constant need to save mass in the design in order to maximize the actual payload that reaches orbit.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA