This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
High-refractive-index-modulation nanocomposites for augmented reality displays

Holographic optical elements (HOEs) are essential in augmented reality (AR) displays, providing benefits such as design flexibility and improved optical efficiency. However, current materials' limited refractive index modulation hampers performance, particularly in achieving a broader field of view and increased brightness.
Addressing these challenges, researchers are now focused on developing materials that can enhance refractive index modulation.
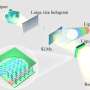
Conducted by a team from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and published in the Chinese Journal of Polymer Science on April 10, 2024, the study showcases a breakthrough in holographic polymer nanocomposites by incorporating the liquid crystal E6M.
This approach significantly improves refractive index modulation while reducing haze, paving the way for more efficient and compact AR devices, and marking a significant advancement in augmented reality technology.
The study's integration of E6M into polymer nanocomposites represents a major advancement. The liquid crystal enhances molecular alignment, achieving a refractive index modulation of 0.050 at 633 nm and maintaining haze at just 5.0% with a 5 wt% concentration.
These enhancements lead to a high diffraction efficiency of 96.2% with a minimal thickness of 5 μm, addressing the challenge of balancing optical performance with material thinness. This makes the composites ideal for next-generation AR devices where efficiency and compactness are crucial.
Professor Hai-Yan Peng, the study's corresponding author, stated, "Our work demonstrates a major improvement in the optical performance of holographic polymer nanocomposites, which could transform AR device design. Achieving high diffraction efficiency with minimal thickness sets the stage for thinner, lighter, and more efficient AR displays."
The advanced holographic polymer nanocomposites offer significant implications for the AR industry, especially in developing future display technologies.
Achieving high optical performance with reduced material thickness and low haze enables the creation of more compact and efficient AR devices. This advancement could drive wider adoption of AR technology across sectors like health care, education, and entertainment, enhancing user experiences and spurring innovation industry-wide.
More information: Meng-Yun Wang et al, Holographic Polymer Nanocomposites with High Refractive Index Modulation by Doping Liquid Crystal E6M, Chinese Journal of Polymer Science (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s10118-024-3110-z
Provided by Huazhong University of Science and Technology