This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
The underrated impact of humidity in predicting heat-related deaths
Governments, medical institutions and other bodies require accurate models on health-related matters in order to better organize their activities.
Climate change has measurable impacts on society, including on human mortality. However, current models to assess the health impacts of climate change do not account for every environmental parameter, especially humidity, which could influence heat stress perceived by the human body, leaving room for improvement.
For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, successfully incorporated humidity data from hundreds of cities into so-called heat stress indicators (HSIs) and assessed their performance in predicting heat-related deaths. The work has been published in PNAS Nexus.
Climate change used to be called global warming for good reason. Broadly, temperatures the world over are rising. However, there are other concerns beyond just air temperature; one of these which is incredibly important in some parts of the world is humidity, the amount of water in the air.
It's important as humidity can affect our ability to cool ourselves down through sweating, when water evaporates from our skin. In high humidity environments, this evaporative cooling is less effective and, after a point, it becomes impossible.
"I'd been investigating the effect of irrigation around urban areas on heat stress, and how it is related to human health," said research fellow Qiang Guo from the University of Tokyo's Department of Global Health Policy.
"Depending on what HSIs you looked at, the results and implications appeared quite different. This discrepancy pushed my team and me to look for the best combination of temperature and humidity which would most accurately estimate human-perceived heat stress. And we wanted to make sure this method would apply to different environments."
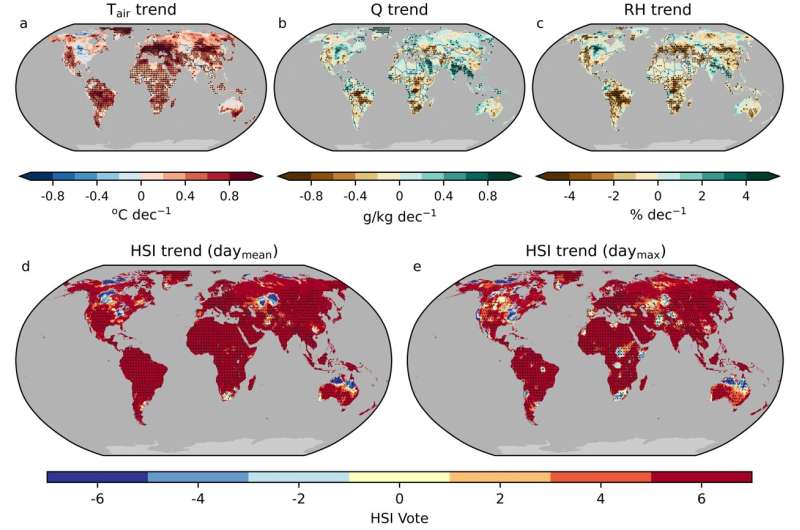
Guo and his team gathered daily human death and climate data, which included air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and incident solar radiation, for 739 cities in 43 countries or territories.
They calculated eight different HSIs based on the climate data. Most HSIs use air temperature and humidity as inputs, while others also include wind speed and solar radiation.
By using sophisticated models called distributed lag nonlinear models and machine learning, the team found the key factor responsible for the performance of HSIs in different locations is the relationship between daily temperature and humidity.
"The effectiveness of HSIs incorporating humidity varies according to geography. We detected locations where humid heat is a more accurate predictor to model heat-related deaths, including coastal and large lake areas of the U.S., Peru, South Korea and Japan. Utilizing HSIs in these regions, such as wet bulb globe temperature, which mimics how humans feel heat, could improve accuracy of heat-health alert systems," said Guo.
"Of course, there are many other factors to consider: for example, socioeconomic issues. Due to data availability, our study mainly focused on the developed regions, and many developing regions under severe heat stress are not included in our analysis.
"Because of this, in the future we plan to collect additional data and conduct analyses for regions in the Global South. Our goal is to better assist people in developing economies in reducing the health impacts of severe heat stress."
More information: Qiang Guo et al, Regional Variation in the Role of Humidity on City-level Heat-Related Mortality, PNAS Nexus (2024). DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae290
Journal information: PNAS Nexus
Provided by University of Tokyo