This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Reconfigurable sensor can detect particles 0.001 times the wavelength of light

In recent years, advances in photonics and materials science have led to remarkable developments in sensor technology, pushing the boundaries of what can be detected and measured. Among these innovations, non-Hermitian physics has emerged as a crucial area of research, offering new ways to manipulate light and enhance sensor sensitivity.
A recent study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus reports a breakthrough in this field, presenting a new type of sensor that leverages exceptional points (EPs) to achieve unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
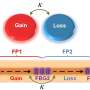
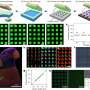
This study introduces a highly sensitive and reconfigurable sensor based on a single spoof localized surface plasmon (LSP) resonator. Exceptional points are unique spectral singularities where eigenvalues and their corresponding eigenvectors converge, significantly boosting the sensitivity of optical sensors.
Traditional EP-based sensors, such as whispering gallery mode (WGM) microtoroids, have demonstrated enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional sensors. However, these sensors face limitations: their EPs are fixed after fabrication, which makes precise adjustments challenging, and they often operate within a narrow frequency range, struggling to detect very small particles due to constraints in perturbation strength and excitation efficiency.
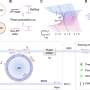
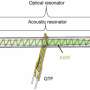
The novel sensor design addresses these issues by incorporating spoof LSP resonators, which simulate the behavior of localized surface plasmons and offer greater flexibility. Suspended above a microstrip line and paired with two movable Rayleigh scatterers, this setup allows for dynamic reconfiguration of EP states across a wide frequency range. This adaptability makes the sensor more robust to fabrication imperfections and enhances its capability to detect extremely small particles.
Key features of the new sensor include:
- Reconfigurability: Adjustable Rayleigh scatterers enable dynamic formation and reconfiguration of EPs, improving the sensor's precision and flexibility.
- Enhanced perturbation strength: Confining electromagnetic fields to the resonator's surface significantly increases sensitivity to perturbations from surrounding particles.
- Multipolar mode excitation: The design supports various plasmonic resonance modes, expanding the sensor's operational bandwidth and detection range.
This advancement represents a significant leap forward in sensor technology, offering exceptional sensitivity for detecting particles as small as 0.001 times the wavelength of light and opening new possibilities for applications in scientific research and industry.
More information: Yaoran Zhang et al, Reconfigurable exceptional point-based sensing with 0.001λ sensitivity using spoof localized surface plasmons, Advanced Photonics Nexus (2024). DOI: 10.1117/1.APN.3.5.056004
Provided by SPIE