This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
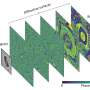
Optimization for inverse problem solving in computer-generated holography
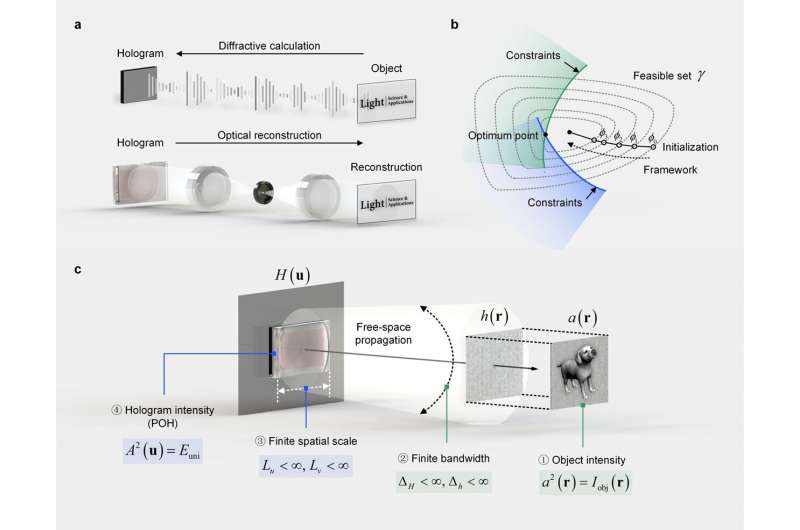
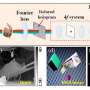
Computer-generated holography (CGH) provides an approach to digitally modulate a given wavefront. This technology, partly inherited from optical holography and partly advanced by the progress of computing technology, has become an emerging focus of academia and industry.
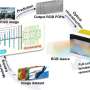
Computer-generated holograms, encoded on various types of holographic media, enable a wide range of applications. Holograms fabricated as diffractive optical elements or metasurfaces can reproduce specific spatial light fields, achieving structured light projection, data storage, and optical encryption. With refreshable devices like spatial light modulators, CGH is able to assist many fields of investigation, including three-dimensional (3D) display, holographic lithography, optical trapping, and optogenetics.
In recent years, CGH has also boosted the birth and growth of potential markets of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), head-up display (HUD), and optical computing. Although the applications and fields of investigation involve various elements and devices, the algorithms for hologram synthesis can be universally applied.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Liangcai Cao from the Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, China, and Professor Daping Chu from the Centre for Photonic Devices and Sensors, University of Cambridge, UK review the optimization algorithms applied to computer-generated holography, incorporating principles of hologram synthesis based on alternative projections and gradient descent methods.
Finding the exact solution of a desired hologram to reconstruct an accurate target object constitutes an ill-posed inverse problem. The general practice of single-diffraction computation for synthesizing holograms can only provide an approximate answer and it is subject to limitations in numerical implementation. Various non-convex optimization algorithms are thus designed to seek an optimal solution by introducing different constraints, frameworks, and initializations.
"Optimization algorithms generate holograms by solving the inverse problem in CGH, but simply optimization does not necessarily guarantee the generation of an appropriate hologram. Careful calculation corresponding to the actual physics process is essential to improve the reconstructing accuracy and produce a hologram as it should be, hence the importance and value of this best practice guide," explained the researchers.
"This review article is focused on the development and implementation of CGH optimization algorithms in real operation, providing a systematical and comprehensive overview from fundamental to actual practice.
"We believe together with our open-source codes which demonstrate all the 2D/3D optimization frameworks presented here, this computation tutorial as well as the incorporated understanding of optimization algorithms for CGH can assist various investigations in the general field of optics" they added.
More information: Xiaomeng Sui et al, Non-convex optimization for inverse problem solving in computer-generated holography, Light: Science & Applications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41377-024-01446-w
Journal information: Light: Science & Applications
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences