This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Power demand peaks in northern India heat wave

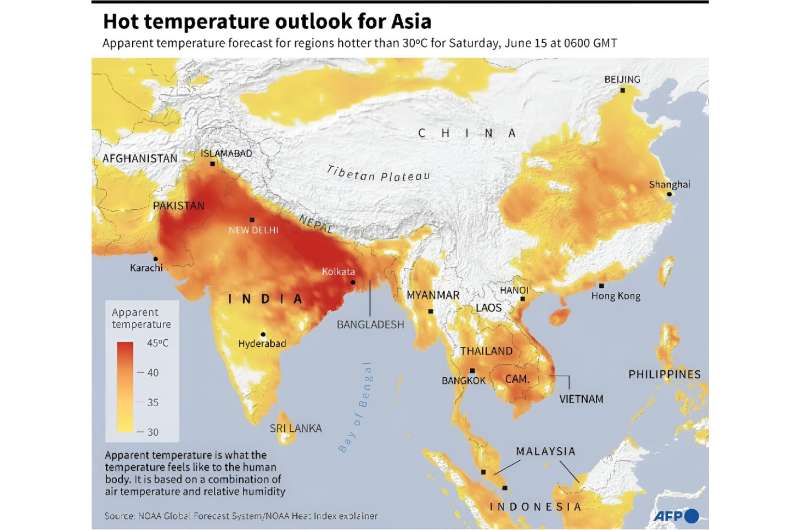
Searing heat wave temperatures in northern India pushed power demand to a record high, the government said Tuesday, with residents of the capital New Delhi also struggling with water shortages.
Much of northern India has been gripped by a brutal month-long heat wave, with temperatures regularly soaring above 45 degrees Celsius (113 degrees Fahrenheit).
Northern India has "been experiencing high demand conditions due to a prevailing heat wave" since May 17, the ministry of power said in a statement, adding it had been forced to import 25-30 percent more power from neighboring regions.
"Despite these challenging conditions, the highest ever peak demand of 89 gigawatts in the northern region was successfully met" on Monday, it said.
India is no stranger to scorching summer temperatures but years of scientific research have found climate change is causing heat waves to become longer, more frequent and more intense.
India is the world's third-biggest emitter of greenhouse gases but has committed to achieve a net zero emissions economy by 2070—two decades after most of the industrialized West.
For now, it is overwhelmingly reliant on coal for power generation.
Authorities have avoided widespread blackouts but there have been multiple localized power outages when supply equipment faltered in the intense heat.
The ministry said it ordered power companies to "maintain a high state of alert and minimize forced outages of equipment".

'Extreme care'
People across Delhi, a sprawling megacity with an estimated population of more than 30 million residents, have been forced to rely on water tankers to meet demand.
The authorities have reduced supply to cope with demand, expanding this week to the city's heart in New Delhi, the base of government offices and the homes of top political leaders.
Delhi relies almost entirely on water supplies from the neighboring agrarian states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
However, given the intense heat and the surge in demand in the respective states, city authorities say they were not supplied enough.
Residents in Delhi also blame politicians for poor planning and under-investment in basic infrastructure.
The India Meteorological Department, the national weather bureau, warned that "heat wave to severe heat wave conditions" are likely to continue until Thursday before gradually easing.

It has repeatedly warned people of the "very high likelihood of developing heat illness and heat stroke in all ages", with "extreme care needed for vulnerable people".
Temperatures are expected to fall as the annual monsoon rains move north this month.
© 2024 AFP