This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
AI model accurately predicts male fruit flies' courtship behavior in response to sight of a female

We've been told, "The eyes are the window to the soul." Well, windows work two ways. Our eyes are also our windows to the world. What we see and how we see it help determine how we move through the world. In other words, our vision helps guide our actions, including social behaviors.
Now, a young Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) scientist has uncovered a major clue into how this works. He did it by building a special AI model of the common fruit fly brain. His work has been published in Nature.
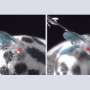
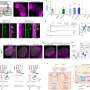
CSHL Assistant Professor Benjamin Cowley and his team honed their AI model through a technique they developed called "knockout training." First, they recorded a male fruit fly's courtship behavior—chasing and singing to a female. Next, they genetically silenced specific types of visual neurons in the male fly and trained their AI to detect any changes in behavior.
By repeating this process with many different visual neuron types, they were able to get the AI to accurately predict how the real fruit fly would act in response to any sight of the female.
"We can actually predict neural activity computationally and ask how specific neurons contribute to behavior," Cowley says. "This is something we couldn't do before."
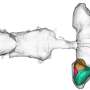
With their new AI, Cowley's team discovered that the fruit fly brain uses a "population code" to process visual data. Instead of one neuron type linking each visual feature to one action, as previously assumed, many combinations of neurons were needed to sculpt behavior.
A chart of these neural pathways looks like an incredibly complex subway map and will take years to decipher. Still, it gets us where we need to go. It enables Cowley's AI to predict how a real-life fruit fly will behave when presented with visual stimuli.
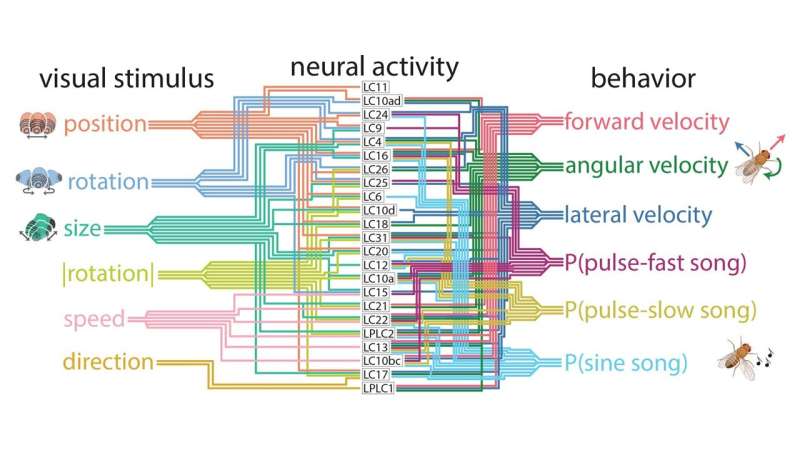
Does this mean AI could someday predict human behavior? Not so fast. Fruit fly brains contain about 100,000 neurons. The human brain has almost 100 billion.
"This is what it's like for the fruit fly. You can imagine what our visual system is like, " says Cowley, referring to the subway map.
Still, Cowley hopes his AI model will someday help us decode the computations underlying the human visual system.
"This is going to be decades of work. But if we can figure this out, we're ahead of the game," says Cowley. "By learning [fly] computations, we can build a better artificial visual system. More importantly, we're going to understand disorders of the visual system in much better detail."
How much better? You'll have to see it to believe it.
More information: Mala Murthy, Mapping model units to visual neurons reveals population code for social behaviour, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07451-8. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07451-8
Journal information: Nature
Provided by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory