This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Could fish ponds help with Hawaiʻi's food sustainability?
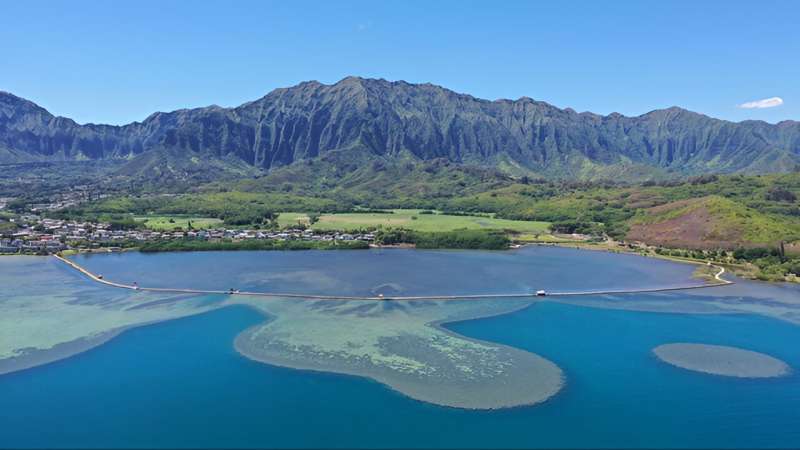

Indigenous aquaculture systems in Hawaiʻi, known as loko iʻa or fish ponds, can increase the amount of fish and fisheries harvested both inside and outside of the pond. This is the focus of a study published by a team of researchers at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB). Today, aquaculture supplies less than 1% of Hawaiʻi's 70 million pounds of locally available seafood, but revitalization of loko iʻa has the potential to significantly increase locally available seafood.
The paper is published in the journal Ecosphere.
According to historical accounts, loko iʻa can create surplus fish inside the pond, but their role as a nursery ground seeding surrounding fish populations has received less attention.
"We have demonstrated the ability of Indigenous aquaculture systems to produce a surplus of fish as well as supplement fisheries in the surrounding estuary," said lead author and marine biology Ph.D. candidate Anne Innes-Gold. "We have heard people voice the idea that historically, loko iʻa provided nursery grounds that may have supplemented fish populations in the estuary. Our study is the first that we are aware of to demonstrate this idea in academic literature."
Hawaiʻi's unique aquaculture system
The Indigenous aquaculture systems found in Hawaiʻi boast a design found nowhere else in the world, and are among the most productive and diverse of their kind. Loko iʻa historically yielded nearly 2 million pounds of fish annually, and hoaʻāina (land tenants) and kiaʻi (caretakers) initially managed them with a "take what you need" mentality to ensure the resource persisted. Most loko iʻa were destroyed in the 20th century, and by 1994 only six of 500 historical loko iʻa were still operating.
"As aquaculture continues to provide a growing proportion of our seafood globally, revival of Indigenous aquaculture systems will be beneficial to sustainably maintain and increase our seafood supply," said Innes-Gold.
Restoration success story
One success story of loko iʻa restoration is the Heʻeia Fishpond, located in Windward Oʻahu and stewarded by Native Hawaiian nonprofit, Paepae o Heʻeia. Their mission is to link Indigenous knowledge with contemporary management to promote cultural sustainability and restore and maintain a loko iʻa for the local community. The benefits of restoring loko iʻa and related systems can help boost local food production, and provide community members with a space to nourish their bodies and minds, connect with ʻāina, practice reciprocity and promote cultural education.
With their foundational work complete, Innes-Gold and her team plan to simulate potential climate change impacts in a loko iʻa system.
More information: Anne A. Innes‐Gold et al, Restoration of an Indigenous aquaculture system can increase reef fish density and fisheries harvest in Hawai'i, Ecosphere (2024). DOI: 10.1002/ecs2.4797
Journal information: Ecosphere
Provided by University of Hawaii at Manoa