This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Germ aversion found to have impacted 2020 election voting behavior
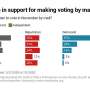
Voters opted to pick candidates in 2020 by mail-in ballots, avoiding poll sites due to COVID-19 concerns rather than because of political party efforts to promote specific voting methods, according to a new University of Michigan study.
Researchers tested attitudes toward using in-person, early, and distanced voting in an experiment during the summer of 2020 and then followed it up by measuring how participants voted in the election. The findings indicate that COVID-19 concerns predicted the use of distanced voting methods more strongly than political party affiliation.
"Democrats have generally favored distanced voting more than Republicans have, but the germ aversion effect here was greater than the party effect," said study co-author Josh Ackerman. "Most voters in this study used absentee methods to cast their votes, suggesting these methods are ones that many citizens want, not just those concerned about disease."
People also disclosed how they planned to vote in future elections—and the results were the same as what happened in 2020. In fact, this voting behavior continued in the recent 2024 Michigan primary. For counties that reported using voting methods examined in the study, 20% more votes were cast absentee/by mail than in person on election day and 12 times more than early in-person voting, the researchers said.
Four months before the 2020 election, 564 participants in several states viewed slideshows framing the pandemic primarily as a health or economic threat. They rated their impressions of voting environments and their attitudes about various voting methods. After the general election, these data were matched to records indicating if and how participants voted.
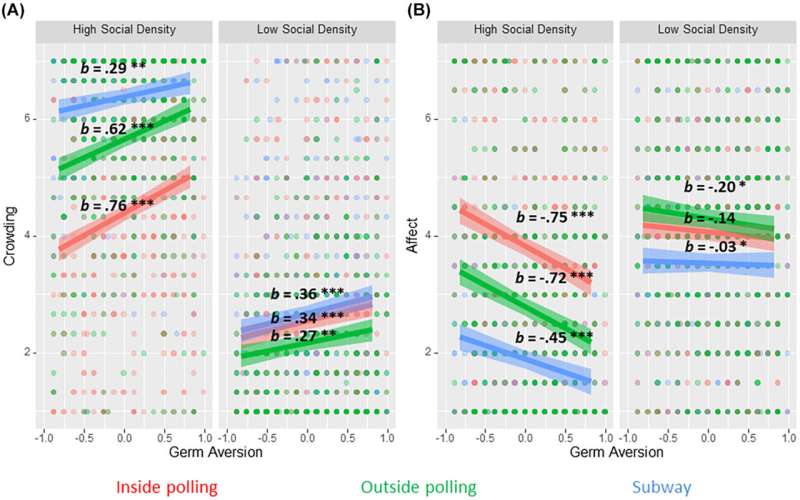
The study showed that exposure to the health consequences of COVID-19 led people to judge crowded polling places more negatively but had few effects on other voter outcomes. Instead, the tendency to chronically worry about germs predicted more negative responses to crowded polling places as well as support for and use of socially distanced voting methods, even when accounting for other relevant factors such as partisanship and local COVID-19 rates.
The research is published in the journal Political Psychology.
More information: Iris M. Wang et al, Crowding at the ballot box: Germ aversion and voting methods in the 2020 U.S. general election, Political Psychology (2024). DOI: 10.1111/pops.12976
Provided by University of Michigan