This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Researchers reveal relationship between air oxidation and air pollution
In the atmospheric environment, the pollutants emitted by human activities are oxidized to secondary pollutants and gradually removed from the atmosphere. Therefore, the understanding of atmospheric oxidation is of great significance for air pollution control.
At present, research on air pollution mainly focuses on analyzing the concentration change and mutual transformation of air pollutants, and there are relatively few studies on the relationship between air oxidation and air pollution.
A research team led by Prof. Gao Xiaoqing from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences used empirical equations to estimate the emission of primary pollutant particles and the formation of secondary pollutant particles in the atmosphere, and they analyzed the change characteristics of major atmospheric oxidants in Lanzhou.
The study is published in Science of the Total Environment.
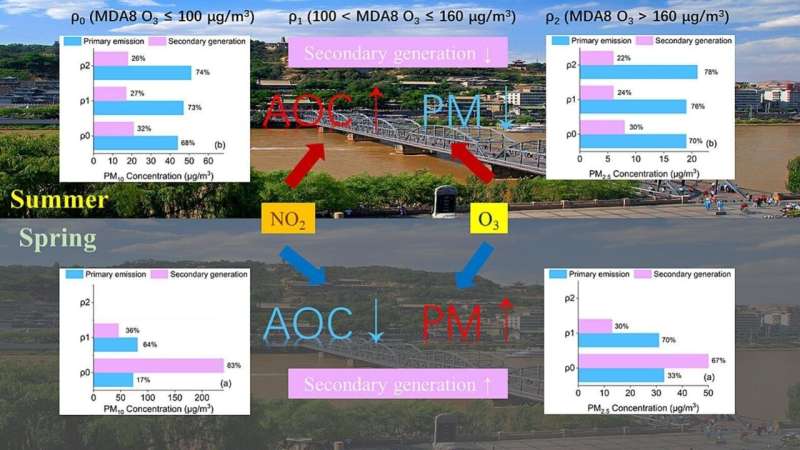
The researchers explored the possible causes of the change in pollutant source and concentration in heavily polluted weather, and elucidated the mechanism of atmospheric oxidation affecting the secondary formation of atmospheric particles.
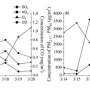
The results show that atmospheric oxidation has a threshold effect on the secondary formation of atmospheric particles. When the concentration of atmospheric oxidant is low (MDA8 O3≤100μg/m3), the oxidation process of atmospheric volatile organic compounds is easier to achieve, thus generating more secondary aerosols and promoting the formation of secondary particles.
When the concentration of atmospheric oxidant is higher than 160μg/m3, the proportion of secondary particulate matter is lower than that of primary particulate matter. The total oxidant agent Ox (Ox=O3+NO2) is negatively correlated with the sulfur oxidation rate and nitrogen oxidation rate, indicating that the formation rate of SO2 and NO2 is inhibited by the high concentration of Ox.
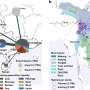
The high-pressure ridge over Lanzhou was maintained for a long time, which reduced the surface wind speed and weakened the transport and diffusion of pollutants near the surface. The PM2.5 in Lanzhou's atmosphere is mainly from the Hexi Corridor area, and the PM10 is mainly from the southeast of Lanzhou.
This study deepens the understanding of atmospheric oxidation affecting the formation mechanism of air pollution, and provides a reference for the prevention and control of air pollution and the improvement of air quality in Lanzhou.
More information: Xiyin Zhou et al, Influence of atmospheric oxidation capacity on atmospheric particulate matters concentration in Lanzhou, Science of The Total Environment (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169664
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences