This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Researchers reveal patterns and mechanisms of unhealthy air pollution event in Lanzhou, China
As a major industrial base and comprehensive transportation hub in northwest China, Lanzhou is an important node city on the Silk Road Economic Belt. Due to its special industrial structure and typical landform, it has long been an important area for atmospheric environment research and management practice.
A research team led by Prof. Gao Xiaoqing from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) analyzed the relationships among the synoptic circulation, regional transportation pollutants and air pollutants based on data from the Atmospheric Comprehensive Observation Station in an unhealthy event in Lanzhou, China.
Their findings were published in Urban Climate on Jan. 31.
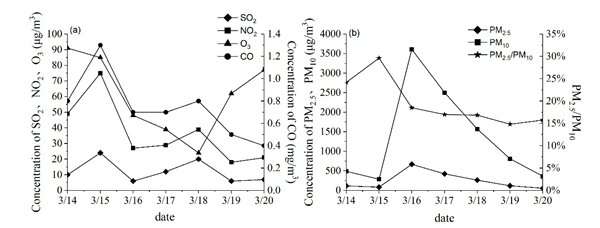
The researchers found that the average value of PM2.5/PM10 was less than 30%, indicating that this event was caused by PM10. The maximum daily average concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were 3,646 μg/m3 and 668 μg/m3, respectively, which was the highest value recorded since they started monitoring (Jan. 1, 2013).
The study showed that the large-scale high-pressure ridge lasted for a long time, and the wind speed at the ground surface was low; the ground surface was prone to long-term calm winds, which reduced the transportation, dilution and diffusion of pollutants.
In addition, there were two areas that contributed more to the concentration of atmospheric particulates during the event. One of them that contributed more to the daily average concentration of PM2.5 was the Hexi Corridor, and one that contributed more to the daily average concentration of PM10 was southeastern Lanzhou.
More information: Xiyin Zhou et al, The pattern and mechanism of an unhealthy air pollution event in Lanzhou, China, Urban Climate (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101409
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences