This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
NASA's Roman telescope to use rare events to calculate expansion rate of universe
Astronomers investigating one of the most pressing mysteries of the cosmos—the rate at which the universe is expanding—are readying themselves to study this puzzle in a new way using NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. Once it launches by May 2027, astronomers will mine Roman's wide swaths of images for gravitationally lensed supernovae, which can be used to measure the expansion rate of the universe.
There are multiple independent ways astronomers can measure the present expansion rate of the universe, known as the Hubble constant. Different techniques have yielded different values, referred to as the Hubble tension.
Much of Roman's cosmological investigations will be into elusive dark energy, which affects how the universe is expanding over time. One primary tool for these investigations is a fairly traditional method, which compares the intrinsic brightness of objects like Type Ia supernovae to their perceived brightness to determine distances.
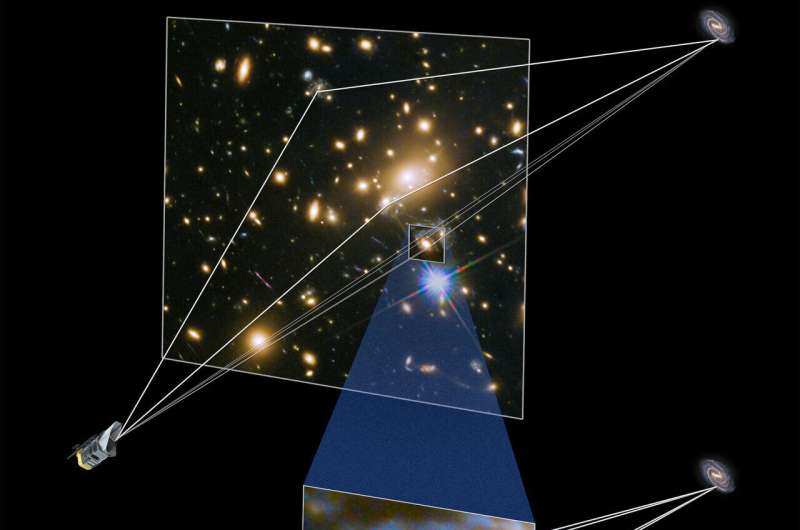
Alternatively, astronomers could use Roman to examine gravitationally lensed supernovae. This method of exploring the Hubble constant is unique from traditional methods because it's based on geometric methods and not brightness.
"Roman is the ideal tool to let the study of gravitationally lensed supernovae take off," said Lou Strolger of the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, co-lead of the team preparing for Roman's study of these objects. "They are rare, and very hard to find. We have had to get lucky in detecting a few of them early enough. Roman's extensive field of view and repeated imaging in high resolution will help those chances."
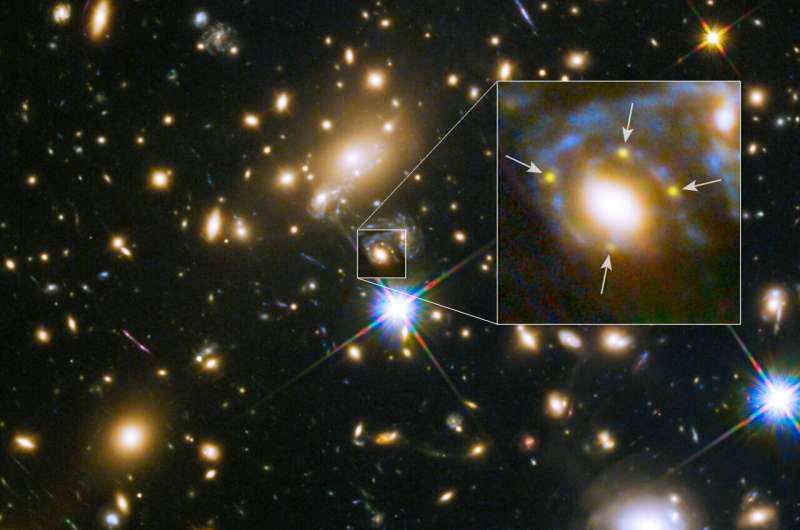
Using various observatories like NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have discovered just eight gravitationally lensed supernovae in the universe. However, only two of those eight have been viable candidates to measure the Hubble constant due to the type of supernovae they are and the duration of their time-delayed imaging.
Gravitational lensing occurs when the light from an object, like a stellar explosion, on its way to Earth passes through a galaxy or galaxy cluster and gets deflected by the immense gravitational field. The light splits along different paths and forms multiple images of the supernova in the sky as we see it.
Depending on the differences between the paths, the supernova images appear delayed by hours to months or even years. Precisely measuring this difference in arrival times between the multiple images leads to a combination of distances that constrain the Hubble constant.
"Probing these distances in a fundamentally different way than more common methods, with the same observatory in this case, can help shed light on why various measurement techniques have yielded different results," added Justin Pierel of STScI, Strolger's co-lead on the program.
Finding the needle in the haystack
Roman's extensive surveys will be able to map the universe much faster than Hubble can, with the telescope "seeing" more than 100 times the area of Hubble in a single image.
"Rather than gathering several pictures of trees, this new telescope will allow us to see the entire forest in a single snapshot," Pierel explained.
In particular, the High Latitude Time Domain Survey will observe the same area of the sky repeatedly, which will allow astronomers to study targets that change over time. This means there will be an extraordinary amount of data—over 5 billion pixels each time—to sift through in order to find these very rare events.
"Because these are rare, leveraging the full potential of gravitationally lensed supernovae depends on a high level of preparation," said Pierel. "We want to make all the tools for finding these supernovae ready upfront so we don't waste any time sifting through terabytes of data when it arrives."
The project will be carried out by a team of researchers from various NASA centers and universities nationwide.
The preparation will occur in several stages. The team will create data reduction pipelines designed to detect gravitationally lensed supernovae in Roman imaging automatically. To train those pipelines, the researchers will also create simulated imaging: 50,000 simulated lenses are needed, and there are only 10,000 actual lenses currently known.
The data reduction pipelines created by Strolger and Pierel's team will complement pipelines being created to study dark energy with Type Ia supernovae.
"Roman is truly the first opportunity to create a gold-standard sample of gravitationally lensed supernovae," concluded Strolger. "All our preparations now will produce all the components needed to ensure we can effectively leverage the enormous potential for cosmology."
Provided by Space Telescope Science Institute