This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists investigate how heat rises through Europa's ocean
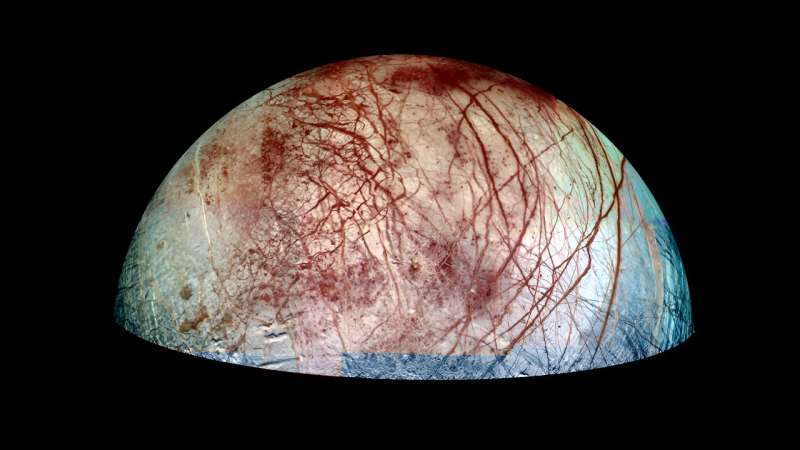
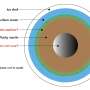
Europa, one of Jupiter's many moons, may be capable of supporting life because its icy surface likely obscures a deep, salty ocean. Europa's ocean is also in direct contact with its mantle rocks, and interactions between rock, water, and ice could provide energy to sustain life.
D. G. Lemasquerier and colleagues examined the way heating from Europa's mantle could drive ocean circulation under the icy crust. The researchers modeled Europa's ocean to further understand how heating patterns from deep inside the moon may affect the thickness of its icy surface. The study is published in the journal AGU Advances.
Mantle heat is one driver of ocean circulation on Europa, and this heating comes in two forms. Radiogenic heating is caused by the decay of radioactive materials in the mantle, and tidal heating is caused by the deformation Europa undergoes as it orbits Jupiter and experiences its strong gravitational pull. Tidal heating is uneven; it's higher at Europa's poles and lower at the points of the moon that are opposite and facing Jupiter.
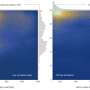
Using simplified idealized modeling that did not consider salinity and ocean-ice feedbacks, researchers examined how heat might transfer from Europa's seafloor, through its ocean, and up to its icy shell. They found that if tidal heating is dominant in the mantle, the latitudinal heat flux variations from the floor would be transferred up through the ocean and remain essentially the same at the ice-ocean boundary, affecting ice thickness and leaving it thinnest at the poles.
However, if radiogenic heating is the dominant type of heating in the mantle, then the ocean would have a relatively small impact on ice thickness. The 2024 Europa Clipper mission could help confirm these model findings and offer new insights into the link between Europa's mantle heating, ocean circulation, and the thickness of its icy crust.
More information: D. G. Lemasquerier et al, Europa's Ocean Translates Interior Tidal Heating Patterns to the Ice‐Ocean Boundary, AGU Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023AV000994
Journal information: AGU Advances
Provided by American Geophysical Union
This story is republished courtesy of Eos, hosted by the American Geophysical Union. Read the original story here.