This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Mathematicians create algorithm that could accelerate IoT by using optimal traffic division
Mathematicians from RUDN University have created a new routing algorithm in the Internet of Things network. It optimally splits traffic, which improves network speed and reliability. The results were published in Mathematics.
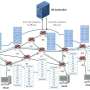
No uniform standards have yet been developed for Internet of Things networks. The architecture of such networks faces multiple requirements: scalability, flexibility, reliability, and availability. To provide all these qualities, efficient routing is necessary.
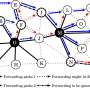
RUDN University mathematicians proposed using a special scheme in which transmission occurs in several ways at once—the traffic flow is split and transmitted through various intermediate nodes. The multipath routing method itself is not new, but the question is the optimal choice of specific traffic paths. There are several approaches to choosing routes for different networks. In some cases, for example, a random selection of paths is used. However, for the IoT network, classical methods are not effective.
"Multipath routing allows data to be transferred faster than single-path routing. The number of possible routes in IoT networks can be large. To choose routes, one needs to solve the problem of traffic distribution," Ammar Muthanna, Ph.D., head of the RUDN University Center for Simulation of Next Generation Wireless Networks said.
The researchers have proposed a new method for multipath routing. It is based on dynamic programming, in which a problem is broken down into simpler subtasks. This reduces the computation time. The created algorithm was compared with random uniform traffic distribution and other classical approaches.
The new method outperforms classical path selection methods in multipath routing, especially for dense IoT networks. The number of intermediate nodes included in the route was reduced by 34%. Computational costs were reduced by 52% and data delivery time by 40%.
"We created a method for selecting optimal routes for the best data transfer that uses dynamic programming. The proposed method increased the efficiency of using network resources. The route selection scheme increased the transmission rate by 40% compared to random traffic distribution. In addition, our algorithm has surpassed the classical ones in terms of energy consumption, packet delivery delay, packet delivery ratio, and costs," said Ammar Muthanna, Ph.D., head of the RUDN University Center for Simulation of Next Generation Wireless Networks.
More information: Abdelhamied A. Ateya et al, Multipath Routing Scheme for Optimum Data Transmission in Dense Internet of Things, Mathematics (2023). DOI: 10.3390/math11194168
Provided by RUDN University