This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
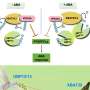
Endosomal stress, a newly defined organelle stress, induces inflammation via ubiquitin signaling
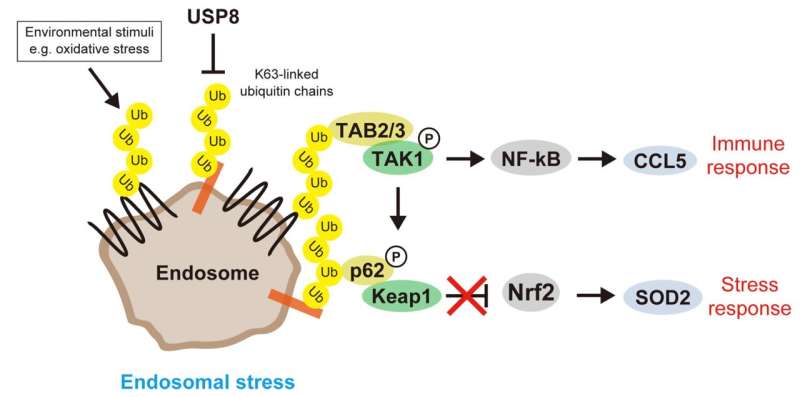
The endosome is an essential organelle located at the center of membrane traffic and mainly sorts plasma membrane proteins internalized by endocytosis in cooperation with ubiquitination, especially lysine-63-linked polyubiquitin chains (K63 ubiquitin chains).
Briefly, ubiquitinated proteins on early endosomes are sequentially recognized by ESCRT complexes (endosomal sorting complexes required for transport-0, -Ⅰ, -Ⅱ, and -Ⅲ) and delivered to late endosomes/lysosomes where they are degraded by acid hydrolases.
Prolonged defects in the endosomal machinery lead to cell death, but the major effects on cellular signaling have been poorly understood. To address this knowledge gap, researchers from various institutions in Japan first considered the abnormal accumulation of K63 ubiquitin chains on defective endosomes as "endosomal stress," an organelle stress, and investigated the cellular responses to endosomal stress caused by depletion of USP8, an essential endosomal deubiquitinase.
The paper is published in the Journal of Cell Biology.
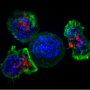
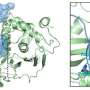
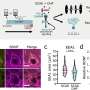
First, the team's proteomic screening revealed that endosomal stress caused by USP8 depletion induces an immune response. Further analysis showed that decoders for K63 ubiquitin chains, such as TAB2/3 and p62, were recruited to endosomes, and consequently activated NF-kB- and Nrf2-mediated gene expression. Upregulated chemokines such as CCL5 were sufficient to transmit the signals to neighboring cells. Furthermore, the team found that oxidative stress, an environmental stimulus that potentially suppresses USP8 activity, induced endosomal stress.
Collectively, the team's results demonstrate that endosomal stress triggers inflammation and that USP8 is a gatekeeper of misdirected ubiquitin signals and inhibits immune and stress response pathways by removing K63-linked ubiquitin chains from endosomes.
In this context, their findings may exemplify the redecoding of K63 ubiquitin chains from membrane trafficking to signal transduction by switching decoder proteins. This achievement will hopefully contribute to the study of organelle stress and ubiquitin-mediated regulation while prompting researchers to explore the physiology and clinical relevance of endosomal stress.
More information: Akinori Endo et al, USP8 prevents aberrant NF-κB and Nrf2 activation by counteracting ubiquitin signals from endosomes, Journal of Cell Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202306013
Journal information: Journal of Cell Biology
Provided by Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science