This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Australian-first study examines impacts of long COVID on intimate partner violence victim-survivors
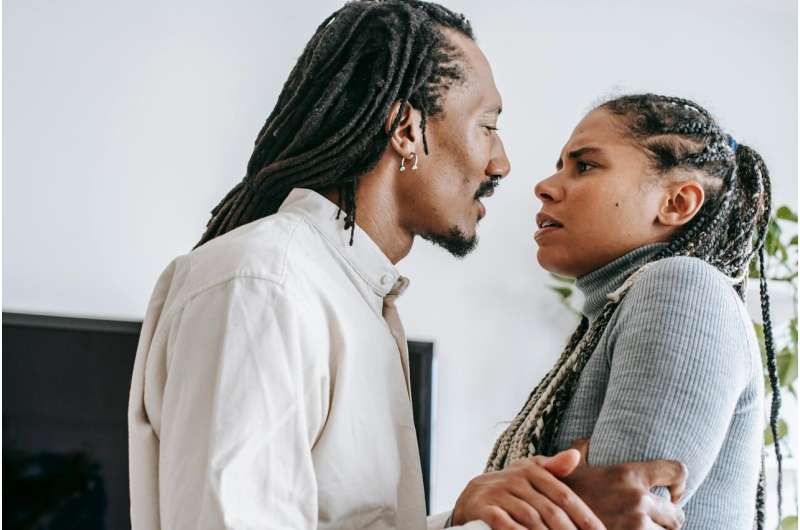

An Australian-first study by researchers at Monash University has examined the impact of long COVID on victim-survivors' experiences of intimate partner violence.
The report Disconnected & insecure: The intersection between experiences of long COVID and intimate partner violence will be launched on Tuesday 23 January at The Wheeler Center with researchers presenting key findings, followed by a panel discussion on women's safety during and beyond the pandemic.
Lead researcher Professor Kate-Fitz-Gibbon said the study addresses a critical gap in global research into how long COVID impacts victim-survivors' safety and support needs.
"Globally there has been no attention paid to the intersection between long COVID and intimate partner violence. As we move further into the new normal of 'living with COVID,' understanding the intense and at times unique recovery needs of victim-survivors of intimate partner violence who have also experienced long COVID is critical to shaping the policy response and ensuring adequate services," Professor Fitz-Gibbon said.
The research team conducted an anonymous national online survey between April and October 2023 with 28 Australian adults who were affected by intimate partner violence and diagnosed with long COVID. The survey findings build new knowledge about the risks, nature and impacts of violence for victim-survivors with long COVID as well as their unique help-seeking behaviors, and support service needs.
The study found 13 of the participants had experienced abuse in a relationship prior to their diagnosis with long COVID, and seven experienced abuse for the first time following their long COVID diagnosis. Eighteen of the survey participants reported that contracting long COVID had put them at higher risk of intimate partner violence.
"What we've heard first hand from victim-survivors is not just changes in the frequency and severity of partner abuse, but also how their partners weaponized their long COVID symptoms to further perpetrate abusive and controlling behaviors," Professor Fitz-Gibbon said.
Professor Fitz-Gibbon co-authored the report with Monash Gender and Family Violence Prevention Center (MGFVPC) researchers Dr. Jasmine McGowan, Dr. Naomi Pfitzner and Benjamin Scott.
"Our study found that the mental and physical symptoms of long COVID placed victim-survivors at an increased risk of abuse. Perpetrators exploited these symptoms to further entrap their victim within coercively controlling relationships," said Dr. McGowan.
The study also provides insights into victim-survivors' help-seeking behaviors and the impact long COVID may have on access to services and supports. For several victim survivors, services were either less accessible or entirely inaccessible due to their long COVID symptoms.
"Nearly half of the victim-survivors who accessed support did so via the phone or a webchat service, highlighting the critical need to ensure continued funding for remote service delivery of domestic and family violence support services," said Dr. McGowan.
The survey also analyzed how experiences of long COVID impact victim-survivors' decisions to remain in an abusive relationship. Several participants said they were too unwell as a result of long COVID to even consider leaving their abusive partner.
According to Professor Fitz-Gibbon the findings provide critical insights that should inform the development of victim-centered supports and services to better support women leaving an abusive relationship, and to prevent escalation and repetition of abuse.
She said the report presents serious policy implications for the Australian Government's National Plan to End Violence against Women and Children, as well as ongoing public health policy and practice.
"Intimate partner violence is the number one risk factor contributing to the disease burden for Australian women aged 18 to 44 years old—greater than alcohol, tobacco and illicit drug use. If the recovery and healing of all victim-survivors is to be better supported, increasing awareness about the risk and recovery needs of victim-survivors with long COVID experiencing abuse must be an integral piece of the National Plan's focus on recovery and healing," Professor Fitz-Gibbon said.
More information: Kate Fitz-Gibbon et al, Disconnected & Insecure: The intersection between experiences of long COVID and intimate partner violence, Monash University (2024). DOI: 10.26180/25000520
Provided by Monash University