This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Webb rings in holidays with ringed planet Uranus
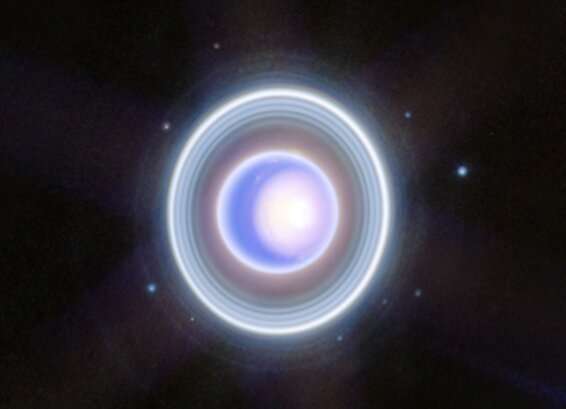

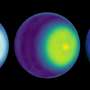
The James Webb Space Telescope recently trained its sights on unusual and enigmatic Uranus, an ice giant that spins on its side. Webb captured this dynamic world with rings, moons, storms, and other atmospheric features—including a seasonal polar cap. The image expands upon a two-color version released earlier this year, adding additional wavelength coverage for a more detailed look.
With its exquisite sensitivity, Webb captured the dim inner and outer rings of Uranus, including the elusive Zeta ring—the extremely faint and diffuse ring closest to the planet. It also imaged many of the planet's 27 known moons, even seeing some small moons within the rings.
In visible wavelengths as seen by Voyager 2 in the 1980s, Uranus appeared as a placid, solid blue ball. In infrared wavelengths, Webb is revealing a strange and dynamic ice world filled with exciting atmospheric features.
One of the most striking of these is the planet's seasonal north polar cloud cap. Compared to the Webb image from earlier this year, some details of the cap are easier to see in these newer images. These include the bright, white, inner cap and the dark lane in the bottom of the polar cap, toward the lower latitudes.
Several bright storms can also be seen near and below the southern border of the polar cap. The number of these storms, and how frequently and where they appear in Uranus's atmosphere, might be due to a combination of seasonal and meteorological effects.
-
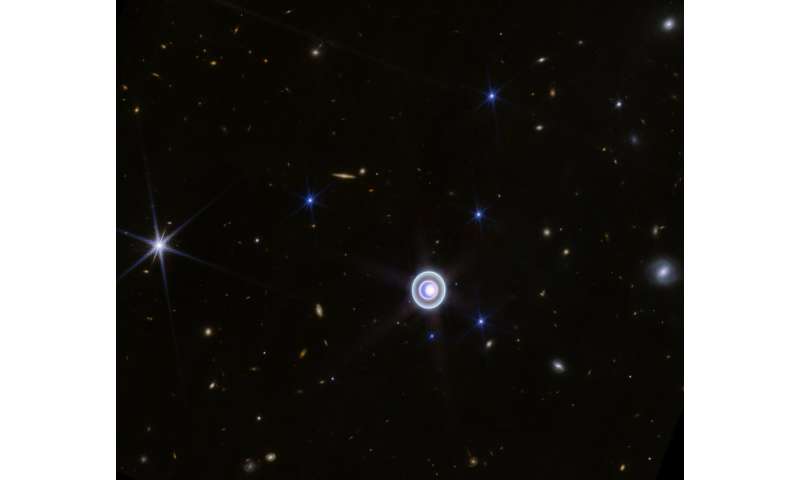

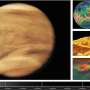
This wide-field image of Uranus from NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope shows the planet amid a smattering of distant background galaxies. This image also includes 14 of the planet's 27 moons: Oberon, Titania, Umbriel, Juliet, Perdita, Rosalind, Puck, Belinda, Desdemona, Cressida, Ariel, Miranda, Bianca, and Portia. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI -

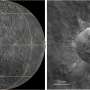
Annotated wide-field compass image of Uranus with some of its 27 moons and a few prominent stars (with characteristic diffraction spikes) labeled. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
The polar cap appears to become more prominent when the planet's pole begins to point toward the sun, as it approaches solstice and receives more sunlight. Uranus reaches its next solstice in 2028, and astronomers are eager to watch any possible changes in the structure of these features. Webb will help disentangle the seasonal and meteorological effects that influence Uranus's storms, which is critical to help astronomers understand the planet's complex atmosphere.
Because Uranus spins on its side at a tilt of about 98 degrees, it has the most extreme seasons in the solar system. For nearly a quarter of each Uranian year, the sun shines over one pole, plunging the other half of the planet into a dark, 21-year-long winter.
With Webb's unparalleled infrared resolution and sensitivity, astronomers now see Uranus and its unique features with groundbreaking new clarity. These details, especially of the close-up Zeta ring, will be invaluable to planning any future missions to Uranus.
Uranus can also serve as a proxy for studying the nearly 2,000 similarly sized exoplanets that have been discovered in the last few decades. This "exoplanet in our backyard" can help astronomers understand how planets of this size work, what their meteorology is like, and how they formed. This can in turn help us understand our own solar system as a whole by placing it in a larger context.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center