This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Traces of sunscreen agents found in the snow at the North Pole
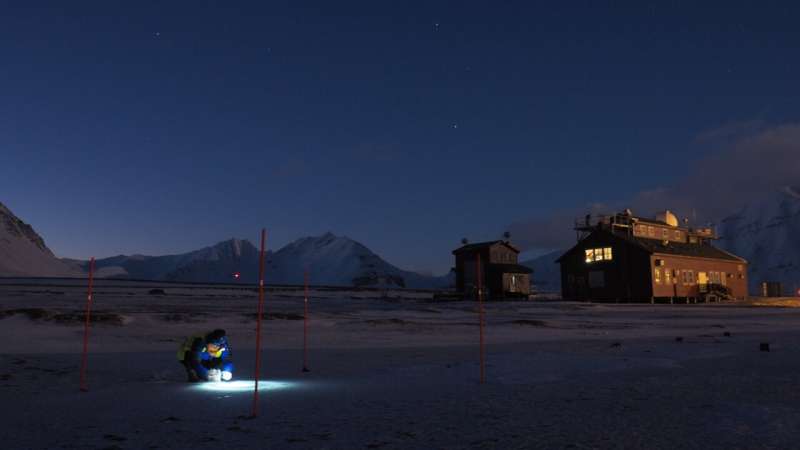

Traces of sunscreen agents were found at the North Pole, on the glaciers of the Svalbard archipelago. They were mainly deposited in winter, when night falls over the Arctic.
A study conducted by researchers from Ca' Foscari University of Venice and the Institute of Polar Sciences—National Research Council of Italy (CNR-ISP), in collaboration with the University Center in Svalbard (UNIS) measured their concentration and investigated their origin. The results are published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
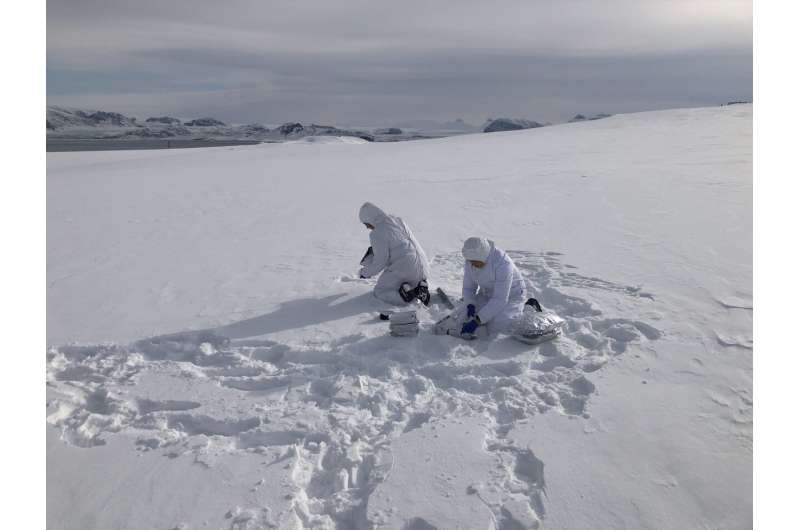
The aim of the work was to present the first overview of the environmental presence of personal care products in the Arctic, providing data on their spatial and seasonal distribution in the snowpack. Thanks to an Arctic Field Grant project in collaboration with CNR-ISP and the Italian research station "Dirigibile Italia" in Ny Ålesund, between April and May 2021 samplings were conducted on five glaciers located across the Brøggerhalvøya peninsula.
The variety of sites, selected near human settlements and in more remote locations, made it possible to study the presence and behavior of emerging contaminants, which are still-in-use compounds, but under scrutiny for their potential harmfulness to the environment. Results revealed the presence at the highest latitudes of various commonly used compounds, such as fragrance materials and UV filters.
"Many of the contaminants we have analyzed, such as Benzophenone-3, Octocrylene, Ethylhexyl Methoxycinnamate and Ethylhexyl Salicylate had never been identified in Arctic snow before," says Marianna D'Amico, a Ph.D. student in Polar Sciences at Ca' Foscari University of Venice and first author of the study.
"The results show that the presence of emerging contaminants in remote areas can be attributed to the role of long-range atmospheric transport," explains Marco Vecchiato, researcher in Analytical Chemistry at Ca' Foscari and co-author of the paper. "In fact, the highest concentrations were found in winter deposition. At the end of winter, contaminated air masses from Eurasia reach the Arctic more easily."
"The most noticeable example concerns certain UV filters normally used as ingredients in sun creams. The highest winter concentrations of these contaminants can only be traced back to the continental regions inhabited at lower latitudes: in Svalbard, during the Arctic night, the sun does not rise and sunscreens are not used," Vecchiato continues.

The distribution of some of these contaminants varies with altitude. Most of the compounds have higher concentrations at lower altitudes, except for Octocrylene and Benzophenone-3. These two UV filters, commonly used in sunscreens, are more abundant on glacier tops where they must have traveled from lower latitudes transported by atmospheric circulation.
These data will be useful for monitoring programs in the area and for the protection of the local ecosystem. Adverse effects caused by the selected contaminants on aquatic organisms have already been detected, such as alteration in endocrine and hormonal system functions. Some of these compounds are subject to regulations in several Pacific islands, and they are under investigation by the European Union.
For the Arctic environmental protection, it will be fundamental to quantify the re-emission of contaminants of emerging concern into the environment during snowmelt. "It will be crucial to understand how these contaminants are transported and deposited in polar areas, especially in relation to variations in local seasonal conditions," concludes Andrea Spolaor, a researcher at CNR-ISP. "Such conditions are rapidly changing in response to climate change, which occurs four times faster in the Arctic than in the rest of the world."
More information: Marianna D'Amico et al, Chemicals of Emerging Arctic Concern in north-western Spitsbergen snow: Distribution and sources, Science of The Total Environment (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168401
Journal information: Science of the Total Environment
Provided by Ca' Foscari University of Venice