This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Astronomers spot giant stream of stars between galaxies
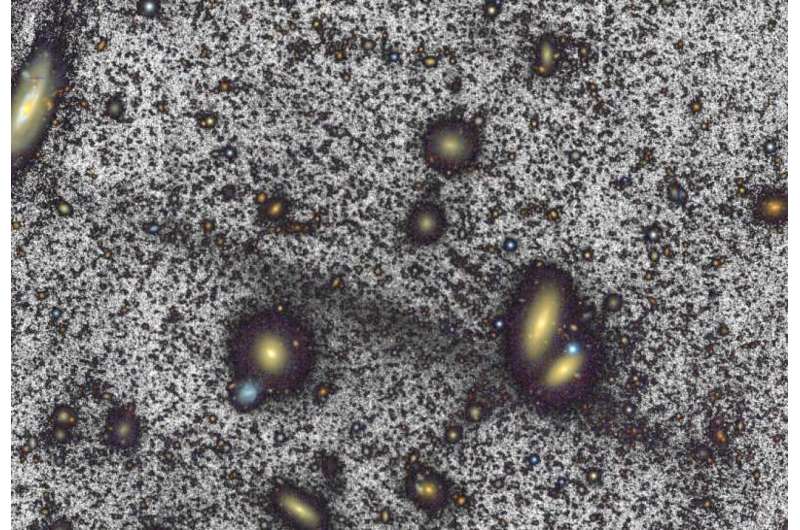
To their surprise, an international team of researchers has discovered a giant and extremely faint stream of stars between galaxies. While streams are already known in our own galaxy and in nearby galaxies, this is the first time that a stream running between galaxies has been observed. It is the largest stream detected to date. The astronomers have published their findings in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The first observations were made with astronomer Michael Rich's relatively small 70-centimeter telescope in California (United States of America). Next, the researchers focused the 4.2-meter William Herschel telescope (La Palma, Spain) on the area. After image processing, they saw an extremely faint stream more than 10 times the length of our Milky Way. The stream appears floating in the middle of the cluster environment, not associated with any galaxy in particular. The researchers have named it the Giant Coma Stream.
"This giant stream crossed our path by coincidence," explains lead researcher Javier Román. He is affiliated with the University of Groningen (the Netherlands) and the University of La Laguna in Tenerife (Spain). "We were studying halos of stars located around large galaxies."
The discovery of the Giant Coma Stream is remarkable because it is a rather fragile structure amid a hostile environment of mutually attracting and repelling galaxies. Co-author Reynier Peletier (University of Groningen, the Netherlands) explains, "Meanwhile, we have been able to simulate such huge flows in the computer. We therefore expect to find more of them. For example, if we search with the future 39-meter ELT and when Euclid starts producing data."
With large future telescopes, the researchers not only hope to discover new giant streams. They also want to zoom in on the Giant Coma Stream itself. "We would love to observe individual stars in and near the stream and learn more about dark matter," says Peletier.
The Coma Cluster is one of the best-studied clusters of galaxies. It contains thousands of galaxies at a distance of about 300 million light-years from Earth in the direction of the northern constellation Coma Berenices. In 1933, Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky showed that the galaxies in the cluster move too fast if you only take the amount of visible matter into account. He figured out that there must be dark matter that keeps things together. The exact nature of dark matter is still unknown.
More information: Javier Román et al, A giant thin stellar stream in the Coma Galaxy Cluster, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202346780, www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202346780. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2305.03073
Journal information: Astronomy & Astrophysics , arXiv
Provided by Netherlands Research School for Astronomy



















