This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers publish first harmonized exposure protocol for ecotoxicity testing of micro- and nano-plastics
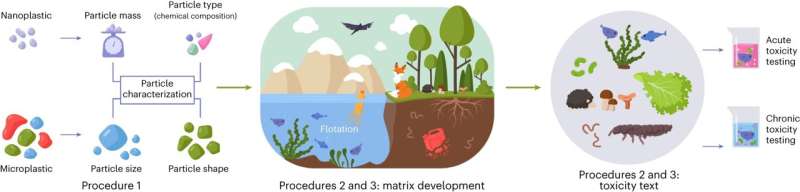
Plastic pollution has become a significant environmental and human health issue at a global scale. Yet despite increasing concern over the harmful effects of micro- and nano-plastics (MNPs), no harmonized guidelines or protocols for their ecotoxicity testing have been available to date.
Current ecotoxicity studies often use commercial spherical particles as models for MNPs, but in nature, MNPs occur in variable shapes, sizes and chemical compositions. Moreover, protocols developed for chemicals that dissolve or form stable dispersions are currently used for assessing the ecotoxicity of MNPs, but these protocols are not optimal for studying MNPs, as plastic particles do not dissolve and also show dynamic behavior in the exposure medium, depending on, for example, MNP physicochemical properties and the medium's ionic strength.
A new exposure protocol, published in Nature Protocols, considers the particle-specific properties of MNPs and their dynamic behavior in exposure systems. The protocol enables the production of more realistic MNPs that resemble those occurring in nature. The protocol also describes exposure system development for short- and long-term toxicity tests for soil and water organisms.
The researchers provide examples of using the protocol to test, for example, MNP toxicity in marine rotifers, freshwater mussels, daphnids and earthworms. The present protocol takes between 24 hours and two months, depending on the test of interest, and can be applied by students, academics, environmental risk assessors and industries.
More information: Fazel Abdolahpur Monikh et al, Exposure protocol for ecotoxicity testing of microplastics and nanoplastics, Nature Protocols (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41596-023-00886-9
Journal information: Nature Protocols
Provided by University of Eastern Finland