This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
JcSEUSS1 shown to play negative role in regulating reproductive growth of Jatropha curcas
In Arabidopsis, rice and tomato, the SEUSS gene encodes a transcriptional adaptor as well as a nuclear localization protein that is widely expressed in many developmental stages and organs. However, the function of SEUSS has not been reported in woody plants.
In a previous study, researchers from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences isolated and cloned a cDNA from Jatropha curcas (a perennial woody oil crop), designated JcSEUSS1. They found that the JcSEUSS1 gene was expressed in almost all tissues of Jatropha, similar to Arabidopsis and rice, suggesting that JcSEUSS1 may be involved in multiple aspects of development and growth in Jatropha
In a study published in Planta, the researchers reported the effect of JcSEUSS1 functions on the reproductive growth stage of Jatropha by systematically overexpressing and silencing the JcSEUSS1 gene.
They found that overexpression of JcSEUSS1 exhibited a negative effect on reproductive growth, and silencing of the JcSEUSS1 gene had a remarkable effect on the development of flowers, fruits, and seeds, resulting in a significant increase in seed yield.
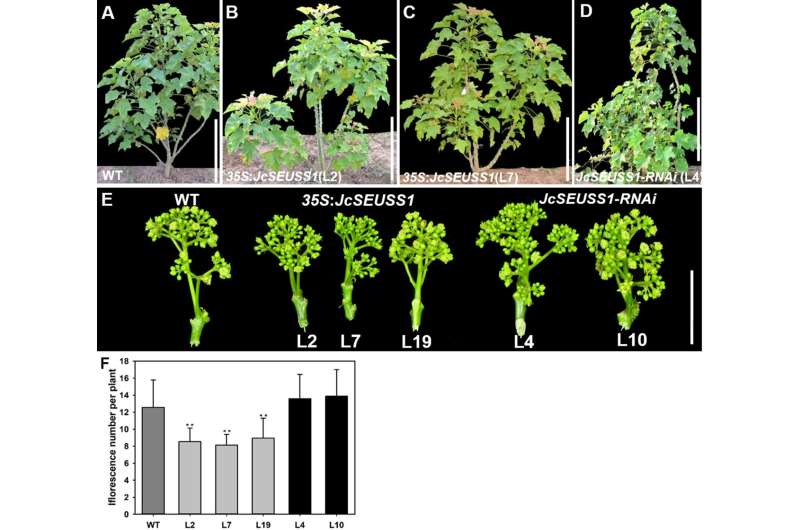
The researchers obtained transgenic Jatropha plants with overexpression and suppression of JcSEUSS1 expression and analyzed the effect of overexpression and downregulation of the JcSEUSS1 gene on phenotypes at different developmental stages.
They found that overexpression of JcSEUSS1 regulated flowering time and flower number per inflorescence but did not affect the morphology of floral organs in Jatropha, while downregulated transgenic lines had no obvious effect on flowering time.
In addition to the phenotypes of flowering time and flower number, transgenic Jatropha overexpressing JcSEUSS1 displayed reduced numbers of infructescences, fruits per infructescence, and seeds per fruit, as well as smaller fruits and seeds.
Collectively, overexpression of JcSEUSS1 had a remarkably negative effect on reproductive growth and development in Jatropha; on the other hand, silencing JcSEUSS1 increased the inflorescence and flower number and resulted in an increase in seed yield.
"Our transgenic technology contributed to a promoted agronomic character for this biodiesel crop," said Tang Mingyong from XTBG.
More information: Jingxian Wang et al, JcSEUSS1 negatively regulates reproductive organ development in perennial woody Jatropha curcas, Planta (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s00425-023-04244-7
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences