This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Exploring optical properties of hollow cirrus clouds for enhanced lidar data interpretation
Researchers led by Prof. Wang Zhenzhu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators have explored the optical properties of hollow cirrus clouds for enhanced lidar data interpretation, with a focus on hollow column ice crystal particles. Their study was published in Optics Express on Oct. 5.
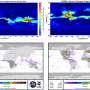
Cirrus clouds cover more than 30% of the global airspace and are one of the key factors affecting the radiation budget balance of the Earth-atmosphere system. Previous lidar detection experiments often ignored the hollow ice crystals in cirrus clouds.
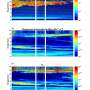
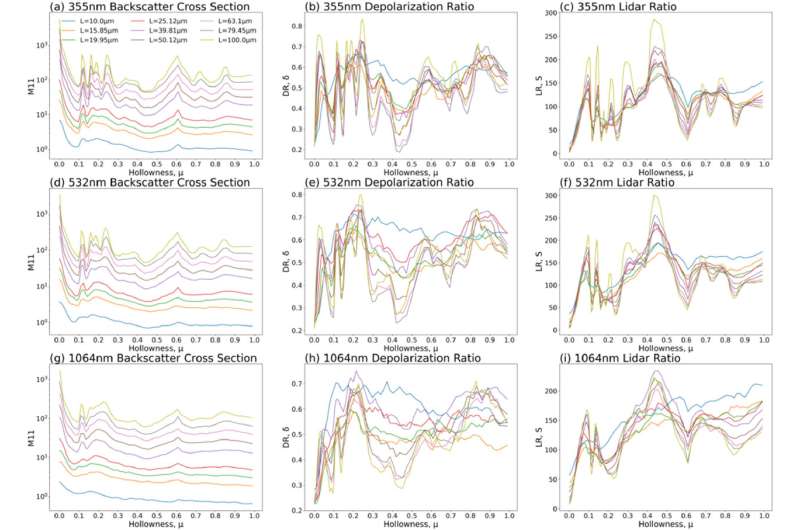
In this study, the research team introduced the concept of "modal hollow columns" (MHC) to better represent the hollow ice crystals found in nature. Using the physical optical approximation method, they calculated the backscattering properties of this randomly oriented model and derived lidar parameters.
They found that when the ratio of MHC to solid columns (SC) exceeded 50%, it was possible to distinguish between the two based on the lidar ratio of 1,064 nm wavelength and the lookup table for the relationship between the color ratio of 1,064/532nm and the depolarization ratio of 532nm.
"A crucial step towards improving the precision and reliability of future lidar measurements is the incorporation of hollow column data into existing databases," said Zhu Xuanhao, first author of the study.
More information: Xuanhao Zhu et al, Backscattering properties of randomly oriented hexagonal hollow columns for lidar application, Optics Express (2023). DOI: 10.1364/OE.502185
Journal information: Optics Express
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences