July 6, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
preprint
trusted source
proofread
Two new sub-Neptunes orbiting nearby stars discovered with TESS
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of two new sub-Neptune exoplanets using NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). The newfound alien worlds, designated TOI-2084 b and TOI-4184 b, orbit nearby M-dwarf stars and are about two and a half times larger than the Earth. The finding was detailed in a paper published June 26 on the preprint server arXiv.
TESS is conducting a survey of about 200,000 of the brightest stars near the sun with the aim of searching for transiting exoplanets. So far, it has identified nearly 6,700 candidate exoplanets (TESS Objects of Interest, or TOI), of which 360 have been confirmed so far.
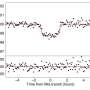
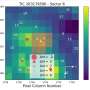
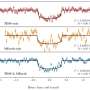
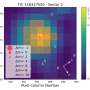
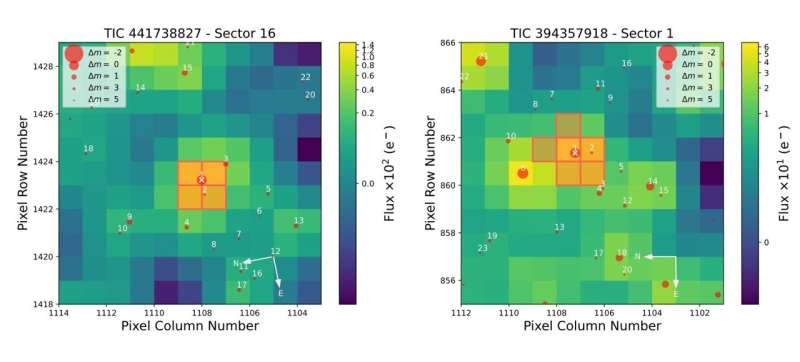
Recently, a group of astronomers led by Khalid Barkaoui of the University of Liège in Belgium, has confirmed another two TOI exoplanet candidates. Using ground-based facilities, they conducted follow-up observations of two stars designated TOI-2084 and TOI-4184, finding that transit signals in their light curves are of planetary nature.
"We presented the validation and discovery of TOI-2084 b and TOI-4184 b by the TESS mission, which were confirmed through follow-up photometric measurements collected by SPECULOOS-South/North, SAINT-EX, TRAPPISTSouth/North, MuSCAT3, LCOGT, Danish and ExTrA telescopes," the researchers wrote in the paper.
According to the study, TOI-2084 b has a radius of 2.47 Earth radii and its predicted mass is estimated to be 6.74 Earth masses. The planet orbits its host every 6.08 days, at a distance of some 0.05 AU from it. The equilibrium temperature of TOI-2084 b was calculated to be about 527 K. The parent star, located 372.6 light years away and estimated to be 7.5 billion years old, has a spectral type M2 and is estimated to be about half the size and mass of the sun.
TOI-4184 b is approximately 2.43 times larger than the Earth and has a predicted mass of about 6.6 Earth masses. The planet has an orbital period of 4.9 days and is separated from its host by 0.034 AU. The equilibrium temperature of this alien world was found to be 412 K. The host star TOI-4184 is of spectral type M5.5, is a quarter the size and mass of the sun, and its age is estimated to be 6.7 billion years. The distance to these stars is estimated to be 225.6 light years.
Based on their properties, TOI-2084 b and TOI-4184 b were classified as sub-Neptune exoplanets. However, although sub-Neptunes the most abundant type of exoplanets, their formation, atmospheric composition, and interior structure are not well understood, as a variety of compositions can match the average density of these worlds. Therefore, the authors of the paper propose further investigation of TOI-2084 b and TOI-4184 b, in order to advance our understanding of sub-Neptunes.
"The small size and proximity of the host stars as well as their brightness in the infrared make them amenable to be further observed by most JWST [James Webb Space Telescope] modes for studying atmospheric compositions," the researchers concluded.
More information: K. Barkaoui et al, TOI-2084 b and TOI-4184 b: two new sub-Neptunes around M dwarf stars, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.15095
Journal information: arXiv
© 2023 Science X Network