This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Space geodetic observations help reveal variations in Earth's surface loads
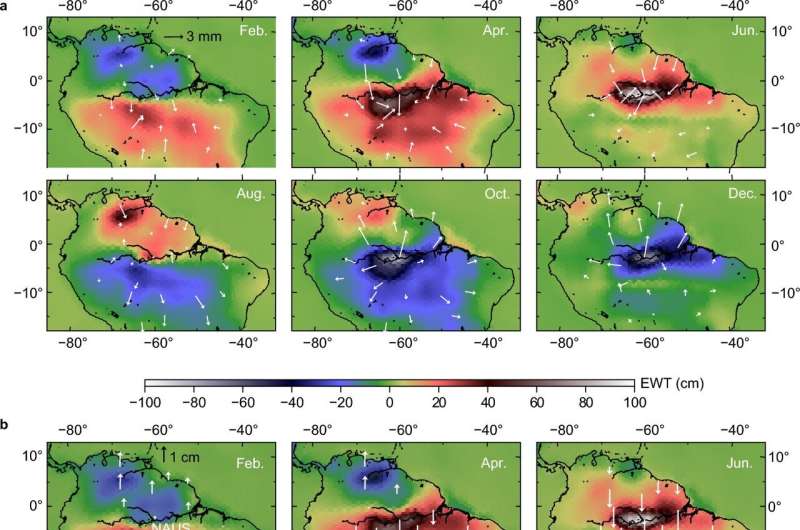
Motion of the Earth's surface mass, including the atmosphere and oceans as well as hydrology and glacier melting, causes the redistribution of Earth's surface loads, deformation of the solid Earth, and variations in the gravity field.
A research team led by Prof. Jin Shuanggen from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has used space geodetic observations to reveal seasonal and intra-seasonal signal variations in the Earth's surface loads.
They investigated displacements from the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and time-variable gravity from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) to extract surface load signals and explore their geophysical applications. The results indicate that space geodesy offers an effective method of studying surface loads and the crustal movements caused by them. The study was published in Satellite Navigation on July 24.
In early days, displacements generated by Earth's surface loads were not large enough to be detected by conventional nonglobal measuring techniques and were thus considered to be noise that disturbed tectonic motion signals. In the 1990s, however, geodesists started observing crustal movements precisely, at high spatial and temporal resolution, using dense networks of continuous GNSS observation stations.
They found significant seasonal signals overlaid on secular tectonic movements, and such seasonal signals gradually drew their attention. The launch of the GRACE satellites in 2002 enabled scientists to directly observe mass anomalies on Earth from space, and the combination of the GRACE and GNSS observations contributed to making surface load studies more convincing.
Previously, the research team had studied seasonal (periodic) and intra-seasonal surface loads using surface displacements from GNSS and mass anomalies from GRACE. They obtained several significant results, e.g., variations in Earth's dynamic oblateness, high-resolution global time-variable gravity fields, extreme droughts in the southwestern United States, and water loads from heavy rains in Japan.
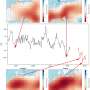
In this study, the researchers presented the long-term and seasonal changes in displacements at GNSS stations and mass anomalies from GRACE in northern South America. They found subsidence and uplift in regions of positive and negative mass anomalies, respectively. On the other hand, GNSS stations moved in the direction from negative to positive mass anomalies. The space geodetic observations have reasonably monitored seasonal changes in land hydrological loads characterized by the alternation of rainy and dry seasons near the equator.
As for the map showing mass anomalies and surface displacements on Hokkaido Island in northern Japan, interannual variations in mass anomalies and amplitudes of seasonal crustal movements well reflected interannual variations in snow amount.
Displacements and mass anomalies from GNSS and GRACE provide complementary information on seasonal changes in surface loads, such as terrestrial hydrological loads. "Due to the different spatial resolutions of the two techniques, displacements and mass anomalies are often inconsistent with each other when surface loads are composed of complex small-scale anomalies. This will be a key direction of future geodetic investigations of surface loads," said Prof. Kosuke Heki, visiting professor at SHAO.
Furthermore, continuous GNSS observation displacements can be used to inverse the time-varying gravity field and monitor water loads anomaly change together with GRACE measurements. "We have obtained tools to study monthly global gravity fields and high temporal-spatial resolution geophysical loads signals and such space geodetic techniques will be important for monitoring disastrous floods and droughts," said Prof. Jin.
More information: Kosuke Heki et al, Geodetic study on earth surface loading with GNSS and GRACE, Satellite Navigation (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s43020-023-00113-6
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences