This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Nutrient enrichment with open canopy decreases trophic redundancy in stream food webs
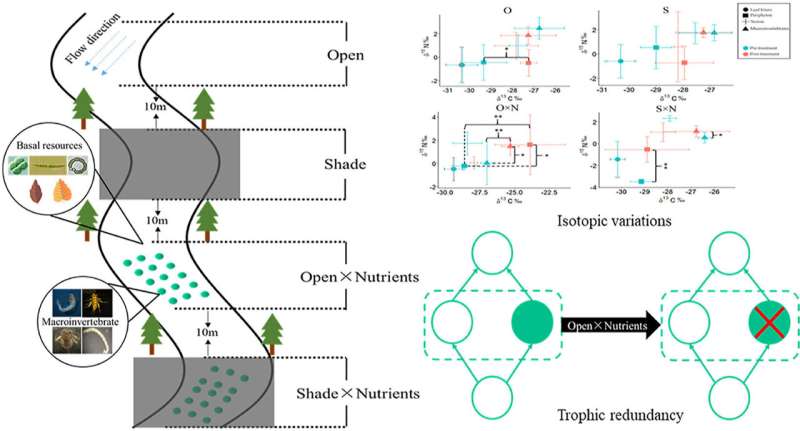
Riparian deforestation has a profound effect on stream ecosystems. The reduction in canopy cover caused by deforestation can increase light intensity and excessive nutrient loads in streams. However, the combined effects of light and nutrients on resource flow and trophic structure in stream ecosystems are not fully understood.
Researchers from the Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated and identified the individual and interactive effects of riparian canopy cover and nutrient pollution on multiple dimensions of the stream food web complexity in three headwater streams in the upper Jinshui River catchment using stable isotope analysis.
Their results were published in Environmental Research, titled "Open riparian canopy and nutrient pollution interactively decrease trophic redundancy and allochthonous resource in streams."
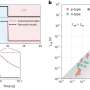
Nutrient enrichment with open canopy treatment increased the dietary contribution of periphyton to macroinvertebrate diets and comparatively reduced the dietary contribution of allochthonous resources (i.e., leaf litter). The increased light intensity and nutrient availability led to an increase in trophic diversity and a decrease in trophic redundancy within the food webs.
Periphyton and macroinvertebrates δ15N values increased with the nutrient enrichment, indicating potential δ15N enrichment of stream benthos by nitrogen pollution.
These results demonstrate the interactive effects of the nutrient enrichment and increased light intensity caused by riparian deforestation on resource flow and trophic structure in stream benthic food webs. It confirms the importance of protecting and restoring riparian vegetation and reducing nutrient inputs to stream ecosystems.
More information: Jian Zhang et al, Open riparian canopy and nutrient pollution interactively decrease trophic redundancy and allochthonous resource in streams, Environmental Research (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116296
Journal information: Environmental Research
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences