This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Study highlights vermiculite as an efficient technique for the remediation of eutrophic lakes
When the amount of nutrients from outside sources is reduced, the release of nutrients already present in the water becomes the main reason for water pollution due to excessive growth of plants and algae. To restore and maintain a healthy balance in lakes affected by this pollution, scientists are focusing on using special mineral-based materials and techniques that involve planting underwater vegetation. These methods have gained popularity as they help promote the long-term recovery of these ecosystems.
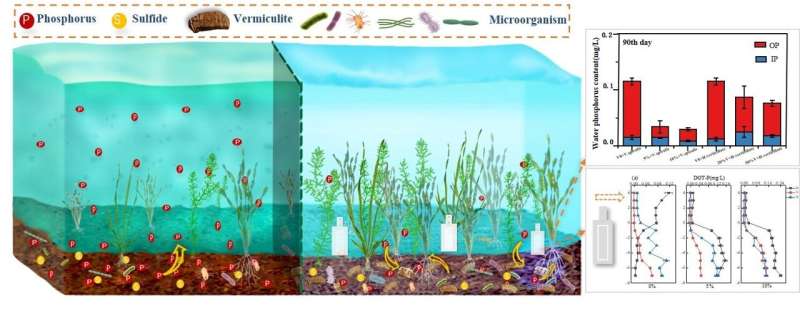
Vermiculite is a natural mineral with a unique structure that can absorb nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as harmful pollutants like heavy metals. It can also help improve the physical makeup of sediment. However, little is known about how sediment is affected when using vermiculite alongside underwater plants.
To address the knowledge gap, a group of researchers from China conducted a study to investigate the impact of combining vermiculite with two types of submerged plants, Vallisneria spiralis and Hydrilla verticillate, on the properties of lake sediment and the structure of the microbial community. The team's findings have been published in the journal Water Biology and Security.
"We found that the concentration of total phosphorus (TP) in the water above the sediment decreased significantly by 63.29%–91.17% when vermiculite was used," said Rou Wang, first author of the study. "Vermiculite may help in controlling the release of unstable phosphorus and enhances the absorption of nutrients by plant roots."
Additionally, the vermiculite-treated sediment showed significantly lower levels of unstable sulfur compared to the control group, indicating that vermiculite can reduce sulfur toxicity for submerged plants.
"Throughout the experiment, the pH of the sediment in all treatment groups remained neutral. However, the oxygen reduction potential (ORP) in the vermiculite-treated group was significantly higher, particularly in the sediment layer between 3 to 6 centimeters," added Wang. "Moreover, the amount of vermiculite added had a positive correlation with sediment pH, ORP, and dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water. These finding suggest that the porous nature of vermiculite enhances sediment permeability and improves oxygen circulation."
Further, the analysis of sediment microbes revealed that the abundance of microorganisms in the 10% vermiculite + Vallisneria spiralis group and 50% vermiculite + Hydrilla verticillate group was 1.67 times and 3.50 times higher, respectively, compared to the control group. Also, the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria, such as Acidobacteria and Proteobacteria, increased significantly and showed a positive correlation with the proportion of vermiculite used, indicating that vermiculite promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
The combined remediation technology of vermiculite and submerged plants effectively improved water quality and sediment properties, thus providing a theoretical reference for its application in lake ecological restoration engineering.
"The combination of vermiculite and submerged plants has proven to be an effective remediation technology that enhances water quality and sediment properties. Our study serves as a valuable theoretical reference for the application of this approach in lake ecological restoration projects," concluded co-corresponding author Yi Zhang.
More information: Rou Wang et al, Synergistic effect of vermiculite and submerged plants on lake sediments, Water Biology and Security (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.watbs.2023.100181
Provided by KeAi Communications Co.