This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Satellites provide crucial insights into Arctic amplification
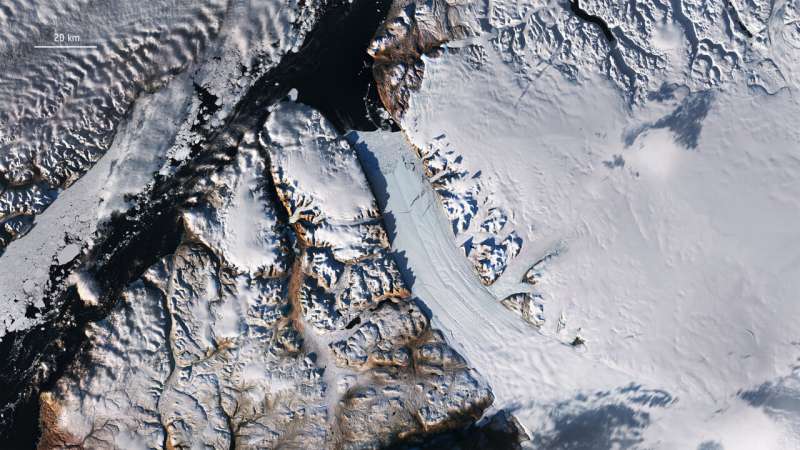

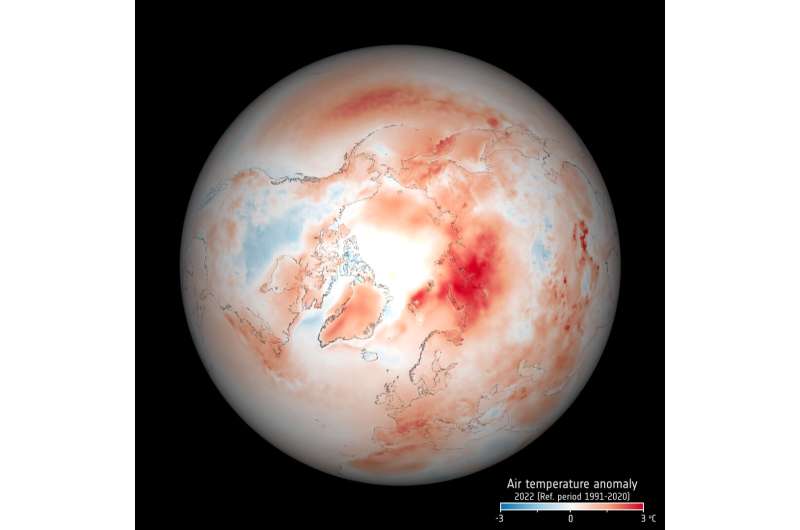
The Arctic, once again at the forefront of climate change, is experiencing disproportionately higher temperature increases compared to the rest of the planet, triggering a series of cascading effects known as Arctic amplification.
As concerns continue to grow, satellites developed by ESA have become indispensable tools in understanding and addressing the complex dynamics at play and the far-reaching consequences for the environment and human societies.
Arctic amplification is the process whereby the Arctic region warms at a faster pace than the global average. This phenomenon is largely attributed to positive feedback mechanisms that exacerbate the effects of greenhouse gas emissions.
This rapid warming is not only destabilizing the delicate balance of the Arctic ecosystem, but is having profound implications for global climate patterns, human populations and wildlife.
ESA's Science for Society Arktalas Hoavva project, which in the northern Sami language means Arctic Ocean, is dedicated to the study of Arctic amplification using satellite data.
A paper published recently in the Remote Sensing journal, describes how satellites have captured this climate phenomenon and how they are proving indispensable for monitoring the remote Arctic region, which is otherwise sparsely measured.

Satellites have witnessed the impact of the amplification on phytoplankton and vegetation productivity as well as on human activity and infrastructure.
For example, in May 2020, an emergency was declared after some 20,000 tons of diesel leaked from a power plant reservoir near Norilsk in Russia. The oil contaminated the Ambarnaya River, which flows into Lake Pyasino—a large body of water.
The disaster, the cost of which exceeded $2 billion, was caused by the collapse of a pillar—it collapsed because the ground had become unstable as a result of thawing permafrost.
Scientists used the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite mission to complement the analysis, field photographs, and historical data to attribute the accident to the Arctic amplification of global warming.
As well as causing problems for infrastructure, when permafrost thaws, it releases large quantities of methane and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, creating a dangerous positive feedback loop that further exacerbates global warming.
The primary driver of Arctic amplification is the demise of sea ice, which has reached unprecedented low levels in recent years.
Sea ice is formed as seawater freezes to form freshwater ice. The freezing process rejects saline water, which is cold and much denser than the surrounding seawater and so sinks to the deep ocean driving global ocean thermohaline circulation.
Without the formation of sea ice, this process will stop and lead to changes in global ocean circulation.
As more ice disappears, the exposed dark ocean surface absorbs more heat, leading to further warming and ice loss.
Furthermore, winds blowing over the exposed ocean surface increase surface waves through frictional coupling. Waves then inhibit refreezing by mechanically eroding the ice as it forms, and this may drive completely new and more energetic ocean circulation patterns across the Arctic Ocean, further tipping the region into a new dynamic state.
ESA's CryoSat and Copernicus Sentinel-3 satellite altimeters measure Arctic sea-ice thickness. The satellites precisely measure the height of ice surfaces relative to the ocean surface between ice leads, enabling scientists to determine ice thickness and volume.
This data has revealed significant declines in Arctic sea ice, particularly during the summer months, highlighting the urgency of the situation. The ESA SMOS satellite complements these data providing measurements of ocean-surface salinity and thin sea ice in the marginal ice zone. These are complemented by Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar imagery providing all-weather sea-ice mapping capabilities. When used together with infrared imagery from Sentinel-3, this is a formidable multi-satellite monitoring capability for the Arctic regions.
In addition to measuring sea ice, ESA-developed satellites have facilitated the observation of other vital parameters, including surface temperature, albedo, and atmospheric composition.
These measurements allow scientists to study the intricate feedback mechanisms that contribute to Arctic amplification. For instance, the Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission provides valuable information on sea-surface temperature, aiding in the analysis of oceanic heat fluxes and their impact on ice melt.
In addition, the melting of the vast Greenland ice sheet, fuelled by Arctic amplification, is contributing to rising sea levels globally. The release of freshwater from melting ice into the North Atlantic Ocean is disrupting oceanic circulation patterns, potentially leading to more extreme weather events such as storms and heatwaves in various parts of the world.
As well as individual satellite missions shedding new light on the remote Arctic, scientists are creating long-term datasets through ESA's Climate Change Initiative. These 40-year-long datasets, complied with data from numerous satellites, enable researchers to study the long-term trends and variations in the Arctic, contributing to a better understanding of the region's response to global warming.
The data collected by ESA-developed satellites not only enhance our knowledge of Arctic amplification, but also support decision-making processes and the development of effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Governments, policymakers, and scientific communities rely heavily on these satellite observations to assess the environmental impact, predict future scenarios, and inform policies for sustainable management of the Arctic region.
The importance of the Arctic is reflected in the Copernicus system that is now evolving to implement new satellite capabilities prioritizing new Arctic measurements that are urgently needed by Copernicus Services, including the dual-frequency CRISTAL altimeter, the Copernicus Imaging multi-frequency Microwave Radiometer (CIMR) and ROSE-L, an L-band synthetic aperture radar mission.
Together with existing Copernicus data, satellite measurements of the Arctic will provide an unprecedented monitoring capability at the time of dramatic changes driven by anthropogenic climate change.
ESA's Craig Donlon said, "The phenomenon of Arctic amplification and its relationship to the global climate emergency serves as a stark reminder that the consequences of climate change are not distant threats but immediate and accelerating crises, impacting not only people living in the Arctic, but ultimately all of us.
"Our paper outlines how satellite observations have captured Arctic amplification as it is developing and with good spatial detail. These observations are indispensable for monitoring of amplification in this remote and inhospitable region that is sparsely sampled by ground observations.
"Satellite data are unique in their ability to capture and monitor environmental transitions in the Arctic region that both precede and follow the emerging impact of Arctic amplification."
More information: Igor Esau et al, The Arctic Amplification and Its Impact: A Synthesis through Satellite Observations, Remote Sensing (2023). DOI: 10.3390/rs15051354
Provided by European Space Agency




















