This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Philosophers agree with economists on climate action, but stress ethical considerations
A new study shows that philosophers with expertise on social discounting and intergenerational distribution want to put more emphasis on the conditions of future generations in climate economic calculations. But they fundamentally agree with economists on one of the key parameters.
How do we value the costs of climate change, which may not be fully materialized for one or two generations? And how much climate action should we do today without wasting resources?
These are some of the questions that economics try to answer in climate economic modeling, and in this context the choice of the social discount rate is crucial. The higher the rate, the more you write down future benefits and costs in areas such as climate change. Conversely, if the discount rate is kept low, more weight is given to the challenges of the future and more climate investments with a long time horizon will make economic sense.
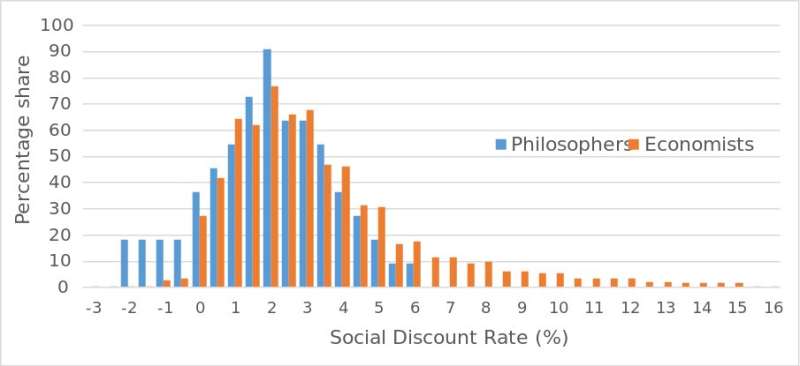
There is a growing consensus among economists to keep the social discount rate around 2%. Now, a new international study shows that many philosophers with expertise on the topic share this recommendation (see image above). The study used a survey to investigate views on the use of discount rates in climate economic models among philosophers with expertise in discounting. A total of 29 philosophers participated in the study, which follows up on a similar survey among economists. The study is published in Nature Climate Change.
This suggests a consensus across two disciplines as different as economics and philosophy on one of the most important parameters in climate economic modeling. This also means that the UN's target of keeping global warming below two degrees is in fact economically optimal when the recommended social discount rate is applied in a recent update to the leading climate economic model (DICE).
The study follows a similar survey of economists. The new survey, which presents the recommendations of philosophers with expertise in discounting, shows that they are more willing to emphasize the ethical aspects involved in long-term issues such as climate change.
It is perhaps less surprising that philosophers focus more on ethics than economists. Still, it is important to account for ethical considerations when economists model far ahead in the future. As Frikk Nesje, Assistant Professor at the Department of Economics and first author of the study, explains:
"For example, how should we weigh the concerns of future generations, and how should we approach the choice between consuming more now or rather in the future? Such questions have an ethical component that many economists today are fully aware of, but not always the best to answer."
Philosophers bring new perspectives to climate economic models
Few philosophers have expertise in discounting compared to economists, and the survey has on the global level only identified 46 relevant philosophers in the field, most of whom, 29, responded to the questionnaire. Of these, almost half did not answer the question on the appropriate level of the social discount rate.
However, almost all respondents have provided written remarks. And while many agree with economists on the numerical value of the social discount rate, philosophers generally express a reluctance to reduce economic modeling of long-term issues such as climate change to a question of economic parameters and classical utility considerations.
One respondent points out that the present generation has an ethical obligation not to harm future generations and suggests a very low discount rate. Conversely, another emphasizes that it is morally acceptable and sometimes even required "to give greater weight to the concerns of those nearer and dearer to us than to those further away."
Both examples represent ethical considerations, which should play a greater role in the climate-economic modeling. Economists shouldn't have a monopoly on policy recommendations, says Nesje.
"The aspects highlighted by the philosophers are already part of the public discourse. For example, the administration of U.S. President Biden has been advised to take non-economic inputs into account when revising the social discount rate. But it is interesting in itself to know what other disciplines think about the issues we are working on."
More information: Frikk Nesje et al, Philosophers and economists agree on climate policy paths but for different reasons, Nature Climate Change (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41558-023-01681-w
Journal information: Nature Climate Change
Provided by University of Copenhagen