Novel electrochemical biosensor for early cancer detection
Exosomes as potential biomarkers in liquid biopsy hold great potential for early cancer diagnosis and monitoring of highly metastatic cancer cells. Recently, a group of researchers proposed a novel electrochemical biosensor for sensitive identification and detection of target exosomes. The biosensor, based on 2D MXene membranes decorated with hierarchical Au nanoarrays, shows satisfactory reproducibility, wide linear range, and high sensitivity for exosome sensing.
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles with a size range of 30–150 nm that derived from tumor cells. Electrochemical biosensors, which are highly sensitive and selective with wide linear range and low cost, can be regarded as a suitable analytical platform for exosome measurement.
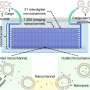
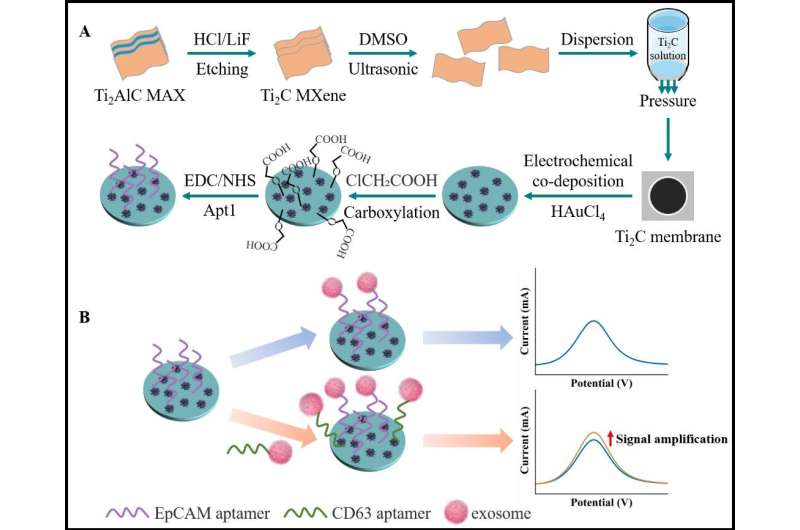
In this work, Dong Wenfei and his team at the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences chose MXene nanosheets, a two-dimensional material with large surface area, high electrical conductivity, and catalytic ability, as the building blocks of MXene membrane preparation via facile vacuum filtration.
The team then introduced Au nanoarrays and grown on the MXene membranes in situ.
"The obtained combination of MXene membrane showed excellent conductivity, a large active site for aptamer immobilization, and accelerated charge transfer," said You Qiannan, first author of the study, a doctoral candidate from SIBET.
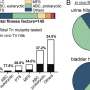
Composite membrane modified by EpCAM recognized aptamer can specifically capture target exosomes. In the meantime, the target exosomes anchor aptamer for CD63, and further enhance the sensing sensitivity and accuracy of the biosensor.
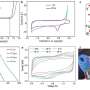
This composite membrane utilized the characteristics of large-scale preparation and MXene membrane reducibility, allowing the biosensor to realize good accuracy and stability in exosome determination.
This work provides a new platform with high sensitivity for accurate detection of exosomes and broadens the application of two-dimensional materials in the field of biosensing, according to Dong.
This work was published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
More information: Qiannan You et al, Hierarchical Au nanoarrays functionalized 2D Ti2CTx MXene membranes for the detection of exosomes isolated from human lung carcinoma cells, Biosensors and Bioelectronics (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114647
Journal information: Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences