Highly-sensitive SERS probes developed to detect the PD-L1 biomarker
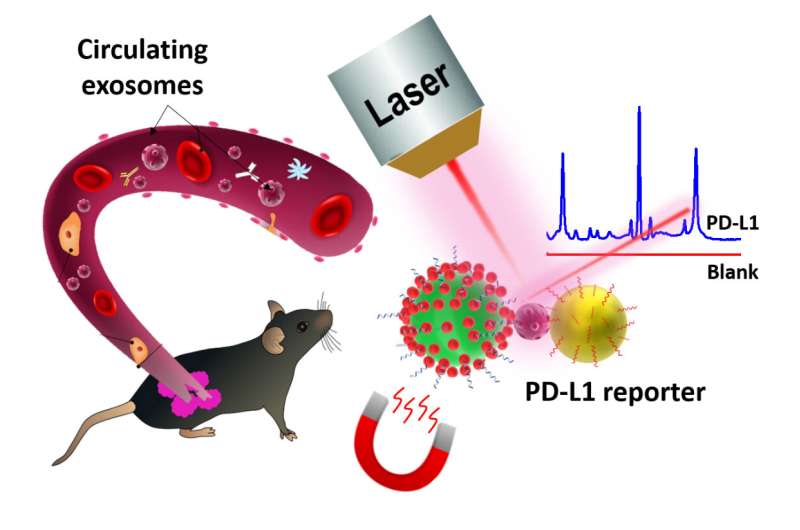
Recently, a team led by Prof. Huang Qing at the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has reported the fabrication of ultrasensitive biosensors based on Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) to detect the cancer metastasis related programmed death ligand (PD-L1) biomarker.
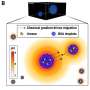
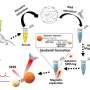
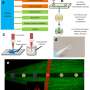
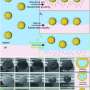
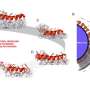
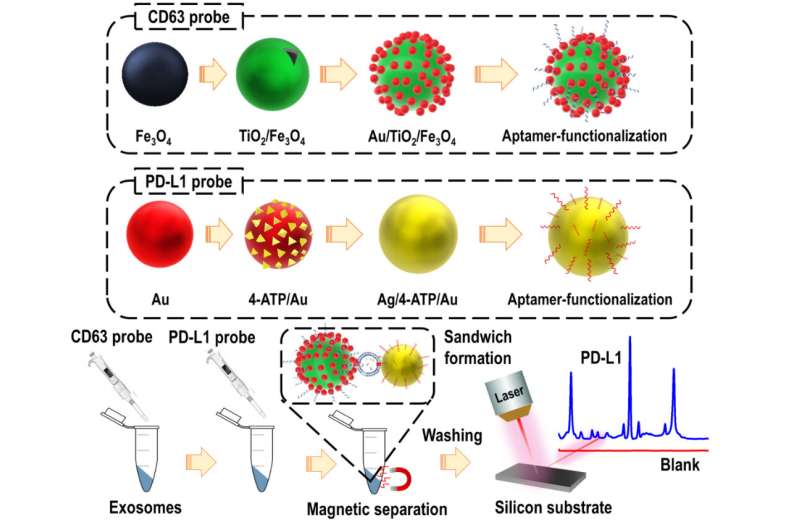
In this research, scientists fabricated highly sensitive and specific aptamer-functionalized probes based on Au/TiO2/Fe3O4 (shell/core) magnetic nanocomposites and Ag/4-ATP/Au (shell/core) SERS nanotags.
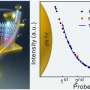
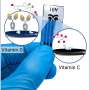
Using the "sandwich" approach, they captured the malignant exosomes between magnetic nanocomposites and SERS nanotags with which they could quantitatively measure the PD-L1 biomarker as low as 4.31 ag/mL by analyzing the Raman report signals.
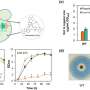
In the mice model, the researchers confirmed that the proposed technique could be useful in analyzing time dependent growth of tumors by analyzing enhancement in PD-L1 expression in tumor.
Moreover, the researchers demonstrated the applicability of their work by integrating nanoparticles probes with a portable Raman spectrometer to realize the PD-L1 measurement with 95% sensitivity.
Overall, the outcome of this work demonstrated the great clinical significance of PD-L1 biomarker diagnosis, which in the future would be helpful in monitoring the health of patients who undergo PD-L1/PD-1 immunotherapy.
The research was published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X.
More information: Muhammad Muhammad et al, Monitoring of circulating exosomal immuno checkpoint in tumor microenvironment through ultrasensitive aptamer-functionalized SERS probes, Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100177
Provided by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences