Team disproves hypotheses about perovskite solar cells, enabling better approaches for targeted optimization
Many hypotheses seek to explain the particularly favorable properties of perovskite semiconductors for solar cells. Polarons or a giant Rashba effect, for example, are thought to play a major role. A team at BESSY II has now experimentally disproved these hypotheses. In doing so, they further narrow down the possible causes for the transport properties and enable better approaches for the targeted optimization of this class of materials.
Research on inorganic and hybrid organic lead halide perovskites has been booming for several years. This class of materials has extremely interesting properties: for example, some perovskite semiconductors also convert the energy-rich blue spectrum of sunlight into electrical energy, so that solar cells based on perovskites in tandem with silicon sub-cells now achieve efficiencies of 30%. Perovskite semiconductors are also suitable for light-emitting diodes, as semiconductor lasers, and radiation detectors. Unlike conventional semiconductors, these materials can be produced cheaply and with little energy expenditure from solutions to yield thin films.
But even after years of intensive research, the microscopic processes in perovskite semiconductors that ensure superior charge transport are not understood in detail. The only thing that is clear is that the charge carriers that are released in the material by sunlight apparently have long lifetimes and are lost less frequently, for example at defects or through recombination.
Researchers have developed hypotheses to explain this behavior, which a team at BESSY II has now tested experimentally. The team led by Prof. Oliver Rader was advised by perovskite expert Prof. Eva Unger at HZB, who also provided the facilities in the HySPRINT laboratory for sample preparation.
Polarons
One hypothesis is that polarons form in lead halide perovskites and contribute to charge transport. Such polarons are oscillations of ions in the crystal lattice which react to the movement of electrons because of their charge. Since perovskites consist of negative (here lead) and positive ions (here cesium), the assumption that polarons play a role was obvious. Measurements by another group also seemed to support this hypothesis.
ARPES-Data: No large Polarons
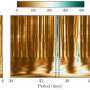
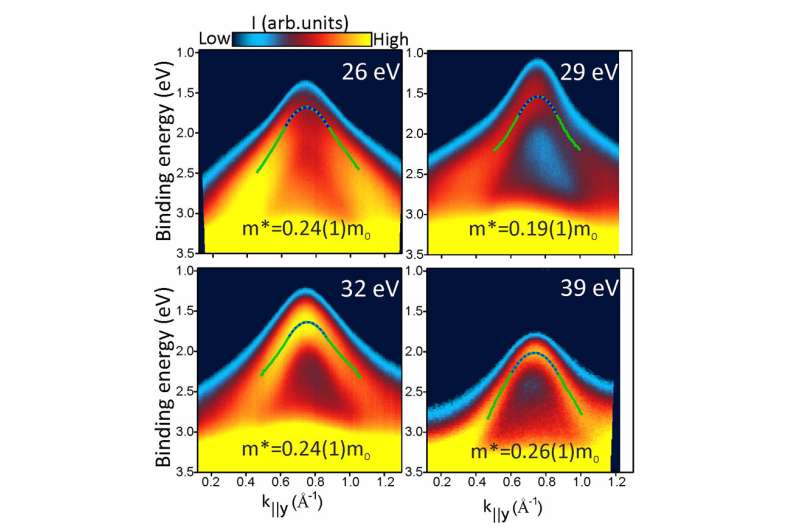
At BESSY II, however, this hypothesis can be tested in detail experimentally. With angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), it is possible to scan the electronic band structures. A weighty share of polarons in the charge transport would become apparent through a higher effective mass. ARPES measures the kinetic energy of the electrons, i.e. 1/2 mv2 with mass m and velocity v. The "tougher" the electron transport, the higher the so-called "effective" mass m. Since the momentum is p = mv, the formula corresponds to a parabola E = (p2)/(2m) which is measured directly in the experiment (see figure): the larger m, the smaller the curvature of the parabola.
However, the measurements Maryam Sajedi carried out on crystalline samples of CsPbBr3 did not show smaller curvatures, thus refuting the hypothesis of large polarons. "The effective mass we determined from the measurement is not larger than theoretically predicted," says Maryam Sajedi. And Oliver Rader explains: "To make sure that we took into account all possible effects other than polarons, for example the repulsion of the electrons from one another, we worked together with theoreticians from Forschungszentrum Jülich. However, there is no increased mass in the experiment for which one would have to postulate polarons."
No giant Rashba effect
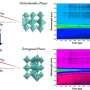
The second hypothesis assumes a giant Rashba effect to limit the losses due to recombination of charge carriers. The Rashba effect is based on a strong spin-orbit coupling that could be produced in lead-halide perovskites by the heavy metal lead. Again, earlier work pointed to this effect as a possible explanation for the long lifetimes of the charge carriers. Maryam Sajedi examined samples of both inorganic CsPbBr3 and hybrid-organic MAPbBr3 with spin ARPES and analyzed the measurement data. "This effect is at least a hundred times smaller than assumed," she comments on the result.
Falsification helps progress
"We have been able to experimentally disprove two common hypotheses about the transport properties in perovskites, which is an important result," says Rader. The elimination of invalid hypotheses is very helpful for the further optimization of those materials.
More information: Maryam Sajedi et al, Is There a Polaron Signature in Angle-Resolved Photoemission of CsPbBr3 ?, Physical Review Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.176405
M. Sajedi et al, Absence of a giant Rashba effect in the valence band of lead halide perovskites, Physical Review B (2020). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.102.081116
Journal information: Physical Review Letters , Physical Review B
Provided by Science and Technology Park Berlin Adlershof