Tailgating is stressful and dangerous: Examining ways it might be stopped
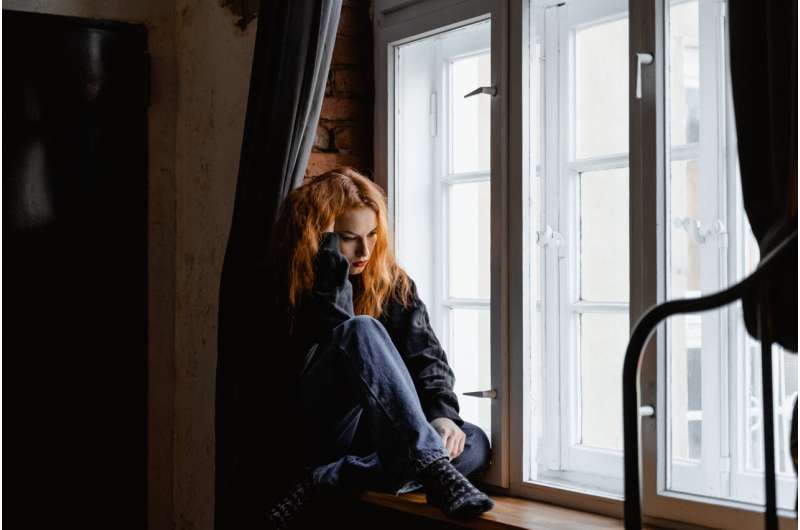

We've all been there (and perhaps even done it): a quick glance in the rear-view mirror shows the car behind is too close to our bumper, an aggression designed to make us drive faster or move over.
It is not only unpleasant, but highly dangerous. A Queensland study found being tailgated is one of the most stressful driving experiences. This is no surprise considering tailgating is among the top five complaints of road users.
So what is being done to prevent this behavior on our roads?
Based on the statistics, one could assume current countermeasures are not effective in preventing tailgating behaviors. For example, over 500,000 motor-vehicle collisions and injuries globally have been attributed to not maintaining a safe following distance.
In Queensland, Australia, over 7,000 injuries and fatalities were attributed to tailgating between 2019 and 2020. However, only 3,120 drivers received an infringement notice for the behavior in this period.
How can tailgating be stopped?
Our research applied three deterrence-based theories used in road safety to examine whether current countermeasures are effective in preventing tailgating.
A total of 887 Queensland licensed drivers completed an online survey (55% male and an average age of 49 years). An alarming 98% of participants reported having tailgated at some point, highlighting how common the behavior is on Queensland roads. Consistent with previous research, males and younger drivers reported the highest levels of tailgating.
Our research made the following findings (based on three deterrence-based theories):
- drivers who believe the consequences for tailgating (that is, the fine and demerit points) are high, are less likely to engage in the behavior
- drivers who frequently tailgate (but are not caught) are more likely to continue the behavior
- those who know of family or friends who have been caught for tailgating are less likely to engage in the behavior
- those who think tailgating increases their risk of injury are less likely to engage in the behavior
- drivers who feel guilty for tailgating are less likely to engage in the behavior
- those who believe the chances of being caught for tailgating are low are more likely to continue engaging in the behavior.
So some current countermeasures for tailgating can be effective. Of particular interest is the finding that individuals who know of someone receiving a fine for tailgating are less likely to tailgate.
And information can spread widely, so someone being fined for tailgating may also deter friends and family from doing it.
However, some findings highlight that there is certainly room for improvement. These findings include:
- drivers believe there is a low chance of being caught for tailgating
- people frequently avoid detection.
Importantly, the findings suggest that legal sanctions can be improved by increasing drivers' perceptions that they will be caught for tailgating.
Our findings also suggest that increasing the penalties (fines and demerit points) for tailgating may not necessarily improve the deterrent effect, as the current penalty is already considered effective.
Where to now?
There are two main actions that could increase drivers' perceptions of the likelihood of being caught for tailgating. These include the use of cameras that can capture this behavior, and additional police operations to detect the practice.
In the UK, there are police operations to detect phone use while driving that use larger vehicles to see what other drivers are doing more easily. UK police also encourage drivers to send in dash-cam footage of drivers violating road rules. Such measures may also be useful for capturing tailgating.
The findings also identify that the risk of injury and sense of guilt associated with tailgating are associated with less frequent engagement in this behavior. So, those who tailgate frequently likely do not feel much guilt about doing so and do not think about the risk of injury associated with crashing. Therefore, campaigns that target these factors is another area to consider for preventing tailgating.
Taken together, the research findings highlight that tailgating remains a pervasive problem. Both legal and non-legal factors need to be part of efforts to counter this behavior.
Tailgating may seem minor, but it is stressful for other drivers and dangerous. We must look at ways to curb this behavior.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()