Savannas suffer greater loss and fragmentation than forests over 30 years in Yunnan

Savannas are ecosystems characterized by a ground layer dominated by grasses and an open canopy of trees that allows direct sun to penetrate to the understory. Several national environmental policies have been put in place in China aiming for landscape protection, but with possible negative consequences for remaining intact savannas in Yunnan.
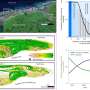
In a study published in Environmental Research Letters, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators analyzed vegetation and land-use change in Yunnan for the period 1986–2016 (30 years of change) using Landsat imagery.
They aimed to assess how much of the savanna vegetation had been lost and fragmented relative to forest and how much savanna remain intact. They further wanted to see which environmental factors were associated to the changes in savanna across Yunnan.
The researchers generated land cover maps of Yunnan for years 1986, 1996, 2006, and 2016, encompassing three decades of change. In 1986, the majority of Yunnan was covered by natural vegetation. By 1996, savannas had a net increase of 2.26%. By 2016, savanna showed an overall decline to 9.34%.
Extensive land cover changes were observed in Yunnan between 1986 and 2016. Fragmentation generally increased for all natural vegetation land cover types from 1986 to 2016, but was more severe for savannas. Savanna coverage declined across the decades mainly due to a drop in open parkland savannas, while forest cover remained stable.
The logistic regression models indicated varying significant associations between the different environmental parameters and land cover changes between and across the three decades. Savannas in more humid environments switched to denser vegetation at a higher rate. Fire slowed the rate of conversion away from savanna states and promoted conversion towards them.
"Considering the low protection presently given to savannas, it is vital to establish protected areas that are savanna-inclusive," said Kyle Tomlinson of XTBG.
More information: R Sedricke Lapuz et al, Greater loss and fragmentation of savannas than forests over the last three decades in Yunnan Province, China, Environmental Research Letters (2021). DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ac3aa2
Journal information: Environmental Research Letters
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences