Thawing permafrost can accelerate global warming

Thawing permafrost in the Arctic could be emitting greenhouse gasses from previously unaccounted-for carbon stocks, fuelling global warming. That is the result of a study conducted by a team of geologists led by Professor Dr. Janet Rethemeyer at the University of Cologne's Institute of Geology and Mineralogy, together with colleagues from the University of Hamburg and the Helmholtz Centre Potsdam—GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences.
In the Siberian Arctic, the research team determined the origin of carbon dioxide released from permafrost that is thousands of years old. This research endeavor is part of the German-Russian research endeavor "Kopf—Kohlenstoff im Permafrost," funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF). The research has been published in Frontiers in Earth Science.
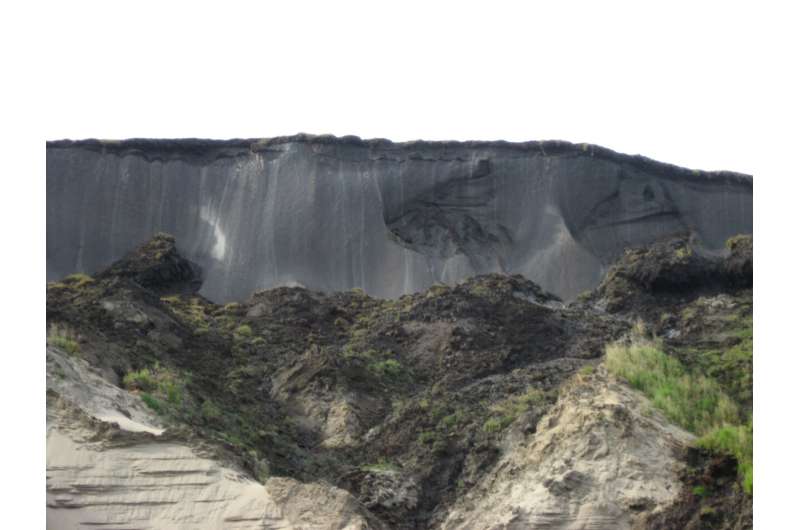
Global climate change is causing temperatures to rise sharply, especially in the Arctic. Among other things, higher temperatures are causing more and more permafrost soils, which have been frozen for thousands of years, to thaw. Particularly affected is so-called 'yedoma' permafrost, which is widespread in areas that were not covered by ice sheets during the last ice age. Yedoma contains up to 80 per cent ice and is therefore also called ice complex. The ground ice can thaw very abruptly, causing the bedrock to collapse and erode. Such processes, known as thermokarst, make carbon previously stored in the frozen ground accessible to microorganisms, which break it down and release it as carbon dioxide and methane. The greenhouse gas release amplifies global warming, which is known as permafrost-carbon feedback.
So far, there are still many uncertainties about the amount of future greenhouse gas release. Among other things, it is not clear how well the ancient carbon that has been frozen in permafrost for thousands of years can be degraded. To find out, the research team took carbon dioxide samples at the Siberian investigation site on the Lena River using specially designed equipment in which carbon dioxide can be stored airtight and transported manner for long periods of time. This is necessary due to the long transport to Germany. Back in Cologne, the researchers then determined the age of the carbon dioxide using the radiocarbon method. In addition, they analyzed the non-radioactive carbon isotopes. Both parameters were then used to calculate how much old and young as well as organic and inorganic carbon had been decomposed in the thawing permafrost.
A large proportion of the carbon—up to 80 per cent—comes from ancient organic matter that was freeze-locked into the sediments more than 30,000 years ago. This means that vegetation remains that died thousands of years ago have been very well 'preserved' in the frozen sediment, making them an attractive food source for microorganisms in the thawing permafrost.
In addition, the team found out for the first time that up to 18 per cent of carbon dioxide comes from inorganic sources. "We did not expect that this previously unnoticed carbon source would account for such a high proportion of the total amount of greenhouse gasses released," said first author of the study Jan Melchert from the University of Cologne. For more precise climate predictions, it would be necessary to take this source into account. Future research will have to clarify where exactly the inorganic carbon in the yedoma comes from and through which processes it is released.
More information: Janet Rethemeyer et al, Sources of CO2 Produced in Freshly Thawed Pleistocene-Age Yedoma Permafrost, Frontiers in Earth Science (2022). DOI: 10.3389/feart.2021.737237/full
Provided by University of Cologne