Evolutions of distribution and driving factors of coastal wetland in Bohai Bay
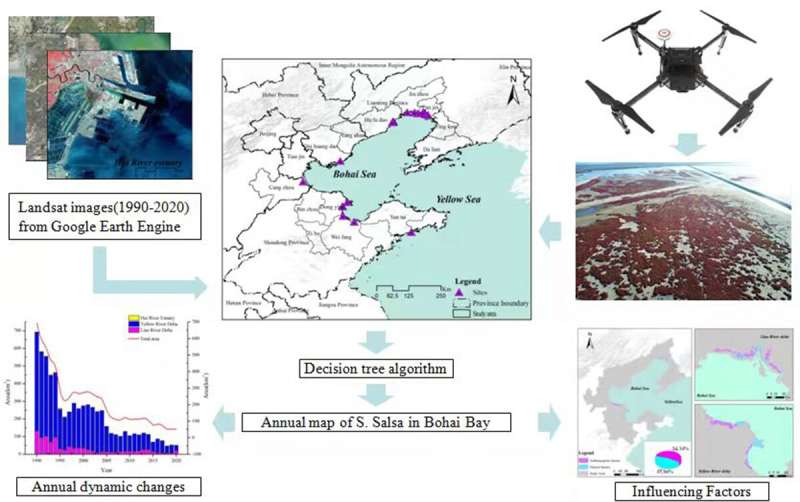
Researchers from the Institute of Applied Ecology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently obtained the annual distribution of Suaeda salsa (S. salsa) using remote sensing data from the past 30 years in Bohai Bay, China. They analyzed influencing factors of S. salsa changes.
Taking Liao River Delta estuary wetland as an example, the changes in land use before and after the utilization of the wetland and the driving factors of ecological environment impacts were also analyzed.
As one of the most vulnerable and economically valuable ecosystems, coastal wetland is highly productive and biologically diverse amid intense human activities. In the 20th century alone, land-use changes caused the loss of 25 to 50 percent of coastal wetlands. Research on coastal wetland changes, influencing factors and eco-environmental effects have attracted wide attention.
Remote sensing technology is an important means to monitor multi-scale and long-term series changes of the coastal wetlands. Based on remote sensing data, the study of coastal wetland change characteristics, influencing factors and ecological environment impact can guide the management, protection and ecological restoration of coastal wetland.
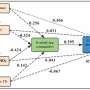
In this study, the researchers found that the area of S. salsa lost about 92.63 percent. Of this, 54.34 percent of the land has been transformed into other land use types by human activities, while 45.66 percent of the land has been degraded into bare land by natural factors. Precipitation, temperature, altitude and distance from coastline were the natural influencing factors of S. salsa distribution.
Meanwhile, the wetland area of Liao River Delta decreased by 669.64 km2, according to the researchers.
What's worse, the value of ecological services has lost US $178 million, the area of suitable habitat for water birds decreased by 1449.49 km2, and cadmium was found to have the greatest risk by potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals.
The wetlands loss, the distribution of cadmium and chromium, rivers and oil wells drove the change of ecological environment effects in Liao River Delta.
More information: Hongyan Yin et al, Evolutions of 30-Year Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Suaeda salsa in Bohai Bay, China, Remote Sensing (2021). DOI: 10.3390/rs14010138
Hongyan Yin et al, Ecological and Environmental Effects of Estuarine Wetland Loss Using Keyhole and Landsat Data in Liao River Delta, China, Remote Sensing (2021). DOI: 10.3390/rs13020311
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences