Human rights to water of millions endangered by large-scale agriculture and industries

In an in-depth cross-country analysis considering the impacts of large-scale agriculture and industry on the human right to drinking water, Dr. Naho Mirumachi, Reader in Environmental Politics, from King's College London has called for renewed political commitment to ensure everyone can enjoy access to clean, drinkable water.
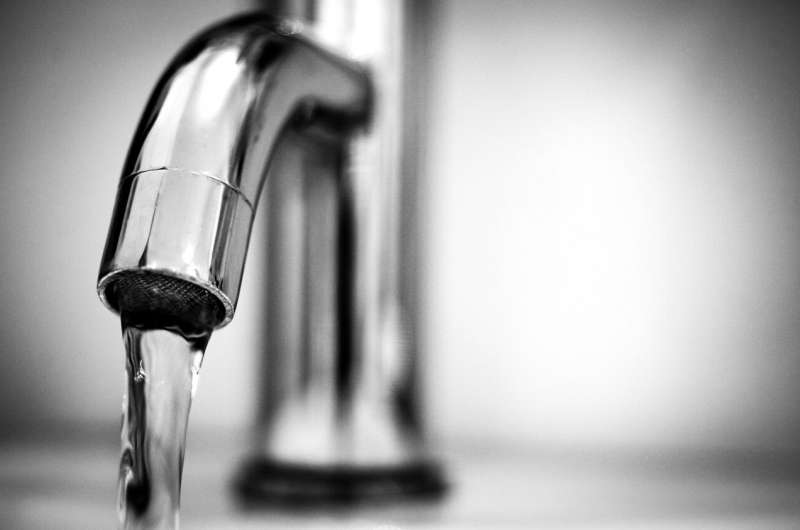
There are Currently 2.2 billion people, or nearly a third of the global population, who lack safely managed drinking water. Of this figure, 450 million children face poor drinking water services and water scarcity, putting them in situations of high or extreme water vulnerability. The labor costs of water collection, including that of time spent to collect water and associated security risks, disproportionately fall on women and girls, affecting 8 out of 10 households without water.
Businesses from the food, textile, energy, industry, chemicals, pharmaceutical and mining sectors contribute to the majority of water use and pollution, which are often facilitated by foreign investment. These sectors are continuing to undertake activities, such as water intensive crop production, and withdraw from fresh water sources in areas where water access is already unreliable at a human cost.
Consumption of one country can have an impact on another because of the global food trade. The water embedded in that food trade or, virtual water 'trade' means that countries are interdependent and have a high water footprint. The UK is the sixth largest net importer of virtual water in the world. Over half of that water footprint comes from countries facing water scarcity. The study, commissioned by the European Parliament's Subcommittee on Human Rights, further highlights:
- It is estimated that global meat consumption will increase by 14% in the next decade as the population increases and income rises. Accordingly, a further 50% increase in food production is required by 2050 to feed the population. This growth in demand for agricultural products will strain the already unsustainable levels of water use.
- Temperature and precipitation changes resulting from climate change will contribute to the uncertainty of water availability and instances of drought and flooding. Water quality will be exacerbated by climate-induced algae blooms
- By 2040, water consumption in the energy sector will increase by about 60%.
- The demand for biofuels is underpinned by global shifts towards cleaner forms of energy. Biofuels impact other water uses, especially when these crops are irrigated for commercial production. There are concerns this will drive up prices and make food less affordable, in particular, for people below the poverty line.
Whilst behavior changes such as eating less red meat would ease pressure on production elsewhere, reduce virtual water 'flows' and relieve water stress, this alone is not enough. It is necessary to strengthen corporate due diligence and corporate accounting. Voluntary mechanisms will only go so far in addressing the impact of businesses on human rights. States need to put in place mandatory measures for corporate accountability.
The analysis was requested by the European Parliament's Subcommittee on Human Rights, funded by the European Parliament, and the copyright is with them. The content of study is the sole responsibility of the authors, and any opinions expressed herein do not necessarily represent the official position of the European Parliament.
More information: The Human Right to Drinking Water: Impact of large-scale agriculture and industry. www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData … A(2021)653649_EN.pdf
Provided by King's College London