Researchers discover Golgi-derived vesicle regulating endosome fission
The endosome has highly dynamic motility and frequently undergoes fission and fusion events to coordinate endocytic trafficking. Endosome fission has been reported to be associated with cargo sorting. After internalization, cargoes can be segregated into distinct domains allocated for their destination, proceeding to either lysosomes for degradation, or the plasma membrane or trans-Golgi network (TGN) for recycling.
Until now, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) network has been recognized as the central regulator that defines where and when endosomes undergo fission. However, whether and how other organelles participate in endosome fission is unknown.
In a study published in Nature Cell Biology, Prof. Li Dong's group from Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with the researchers from Tsinghua University, reported a novel function of the Golgi apparatus derived SEC14L2 compartment in regulating the ER-associated endosome fission, and demonstrated that the coordinated interactions among distinct intracellular membrane systems are crucial for precisely executing the biological function.
The researchers characterized SEC14L2 compartment, a Golgi-derived vesicle, through the combination of super-resolution live-cell imaging system and electron microscopy. When the inhibitor BFA was applied to block the formation of this vesicle, ER-associated endosome fission is significantly delayed, causing endosomes with enlarged and tubulated morphology. This phenomenon indicates the potential role of the Golgi apparatus in ER-assisted endosome fission.
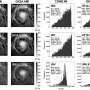
To observe the dynamics of SEC14L2 compartment, ER and endosomes, the researchers employed the grazing incidence structured illumination microscopy (GI-SIM). They found that SEC14L2 compartment frequently contacted with ER and endosomes.
During endosome fission, SEC14L2 compartment was recruited and stabilized onto the dividing site where ER tubule across. Meanwhile, it facilitated the PtdIns3P accumulation and PtdIns4P removal on endosome membrane. Only after endosomal PtdIns4P to PtdIns3P conversion was done, an endosome proceeded its division.
Mechanically, SEC14L2 protein enriched in the Golgi-derived vesicle, plays a cardinal role in regulation endosome fission. On one hand, SEC14L2 directly binds PtdIns3P and PtdIns4P that directs their transfer among liposomes in vitro. On the other hand, it interacts with the PI3K and activates it to promote PtdIns3P generation.
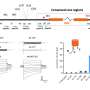
When knocking out SEC14L2 protein in the COS-7 cells, a significant reduction of endosomal PtdIns3P level and abnormal accumulation of endosome PtdIns4P was demonstrated, resulting in delayed endosome fission and enlarged endosome, consistent with observations upon depletion of the SEC14L2 compartment.
To validate involvements of SEC14L2's lipid binding activity in endosome fission, the researchers performed rescue experiments, and found that the lipid-binding deficient form, SEC14L2-M5, failed to rescue endosome fission defects in SEC14L2 KO COS-7 cells, while wild-type SEC14L2 form successfully rescue this phenotype.
This study showed that the lipid-binding activity is essential for SEC14L2-mediated endosome fission. It is worth noting that another study published earlier in Science also reports the function of the Golgi-derived vesicle in regulating ER-associated mitochondrial fission. These two studies highlight an unanticipated role of the Golgi network in intracellular membrane homeostasis. Further research is needed to demonstrate the identity of these Golgi-derived vesicles.
More information: Bo Gong et al, A Golgi-derived vesicle potentiates PtdIns4P to PtdIns3P conversion for endosome fission, Nature Cell Biology (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41556-021-00704-y
Journal information: Nature Cell Biology , Science
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences