Scientists invent an artificial nose for continuous bacterial monitoring
A team of scientists at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have invented an artificial nose that is capable of continuous bacterial monitoring, which has never been previously achieved and could be useful in multiple medical, environmental and food applications.
The study was published in Nano-Micro Letters.
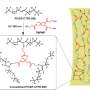
"We invented an artificial nose based on unique carbon nanoparticles ("carbon dots") capable of sensing gas molecules and detecting bacteria through the volatile metabolites the emit into the air," says lead researcher Prof. Raz Jelinek, BGU vice president for Research & Development, member of the BGU Department of Chemistry and the Ilse Katz Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology, and the incumbent of the Carole and Barry Kaye Chair in Applied Science.
The patent-pending technology has many applications including identifying bacteria in healthcare facilities and buildings; speeding lab testing and breath-based diagnostic testing; identifying "good" vs. pathogenic bacteria in the microbiome; detecting food spoilage and identifying poisonous gases.
"BGU has a remarkable track record of sensor development, which has infinite possibilities for real-life application," says Americans for Ben-Gurion University (A4BGU) Chief Executive Officer Doug Seserman. "Our renowned multi-disciplinary research efforts continue to ignite innovation, addressing some of the world's most pressing issues."
The artificial nose uses chemical reactions and electrodes to sense and distinguish vapor molecules and record the changes in capacitance onto interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) coated with carbon dots (C dots). The resulting C-dot-IDE platform constitutes a versatile and powerful vehicle for gas sensing in general, and bacterial monitoring in particular. Machine learning can be applied to train the sensor to identify different gas molecules, individually or in mixtures, with high accuracy.
More information: Nitzan Shauloff et al, Sniffing Bacteria with a Carbon-Dot Artificial Nose, Nano-Micro Letters (2021). DOI: 10.1007/s40820-021-00610-w
Provided by Americans for Ben-Gurion University