Restoring the filtration efficiency of N95 masks after they have been cleaned
N95 masks are a critical part of the personal protective equipment used by front-line health care workers. These masks achieve 95% efficiency at filtering out tiny 0.3-micron particles, while maintaining reasonable breathability, thanks to a layer of fine melt-blown polypropylene fibers incorporating electrical charges to attract particles.
Extended usage and decontamination provoked by severe supply shortages around the globe during the COVID-19 pandemic can easily remove the charges and degrade filtration efficiency.
In the journal Physics of Fluids, researchers from India's Tata Institute of Fundamental Research and Israel's Technion-IIT share a method to restore the filtration efficiency of N95 masks to out-of-box levels—as long as the mask is not structurally compromised.
"Today, N95 masks are being worn by health care workers for extended periods," said co-author Shankar Ghosh. "This gives rise to very humid conditions, and humidity is detrimental to electrostatics."
During use, all electrostatics-based masks slowly lose their efficiency due to humidity.
"It's much worse in a place like Mumbai during the Indian monsoon, where ambient humidity levels can reach more than 90%," Ghosh said.
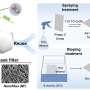
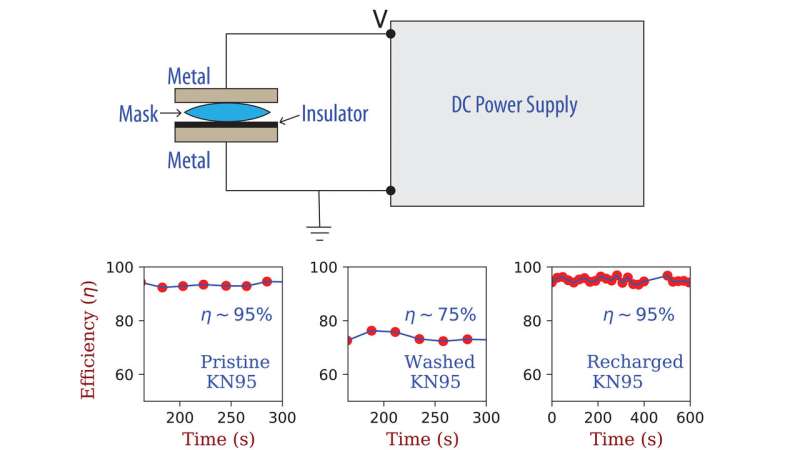
The group's work exploits that, under high electric fields, the polypropylene conductivity is high, which makes introducing excess charges into the material possible by connecting it to a battery. When the charge source is switched off, the applied electrical field becomes zero, and the conductivity of the polypropylene drops effectively to zero. As a result, the added charge carriers immobilize, and the material remains charged.
The researchers discovered they could toss an N95 into a standard washing machine to clean it, which significantly reduces its filtration efficiency. They could then recharge it by sandwiching it between two electrodes at high voltage to recover its 95% efficiency.
"We've also shown a proof-of-concept construction of a battery-operated smart mask, where the lost charge gets replenished periodically by plugging the mask into a charging station—akin to how you would charge your smartphone," Ghosh said.
The group believes its method to keep masks charged will lead to highly energy-efficient smart masks.
"Currents are in microamps, and the power requirement is extremely low, on the order of a milliwatt, so a compact and practical solution may soon be feasible," said Ghosh.
Beyond this, their method will be useful for a variety of air filtration applications, such as HVAC or industrial filters.
More information: "Recharging and rejuvenation of decontaminated N95 masks," Physics of Fluids, aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0023940
Journal information: Physics of Fluids
Provided by American Institute of Physics