Image: Sculpted by nature on Mars
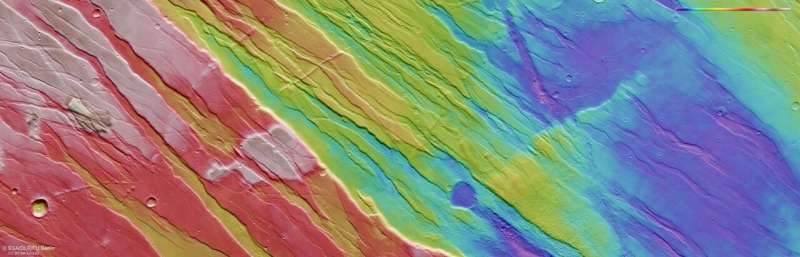
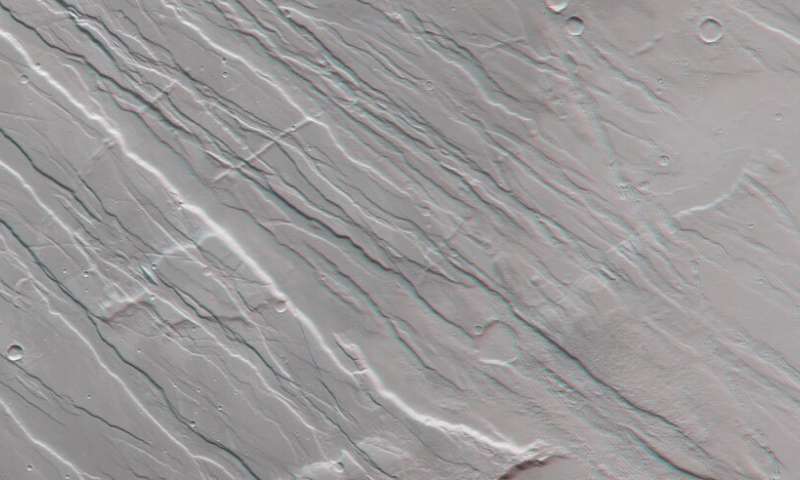
Nature is a powerful sculptor—as shown in this image from ESA's Mars Express, which portrays a heavily scarred, fractured Martian landscape. This terrain was formed by intense and prolonged forces that acted upon Mars' surface for hundreds of millions of years.
Features on Mars often trick the eye. It can be difficult to tell if the ground has risen up towards you, or dropped away. This is a common phenomenon with impact craters especially, and is aptly named the "crater/dome illusion"; in some images, craters appear to be large domes arching up towards the viewer—but look again, and they instead become a depression in the surrounding terrain, as expected.
Such a phenomenon is at play in this image from Mars Express, which shows part of Tempe Fossae, a series of faults that cuts across the region of Tempe Terra in Mars' northern highlands.
Upon first glance, it is difficult to tell if ground is rising up, sinking down, or a mix of both. The landscape here is scratched, scored, and wrinkled: ridges slice across the frame, interspersed with the odd impact crater, and the entire region is full of cliffs and chasms.
The terrain here belongs to the volcanic Tharsis province, also known as Tharsis rise, which is located close to the planet equator, at the boundary between low plains in the Northern hemisphere and highlands in the South, and displays a complex geology originating from the processes involved in its formation.
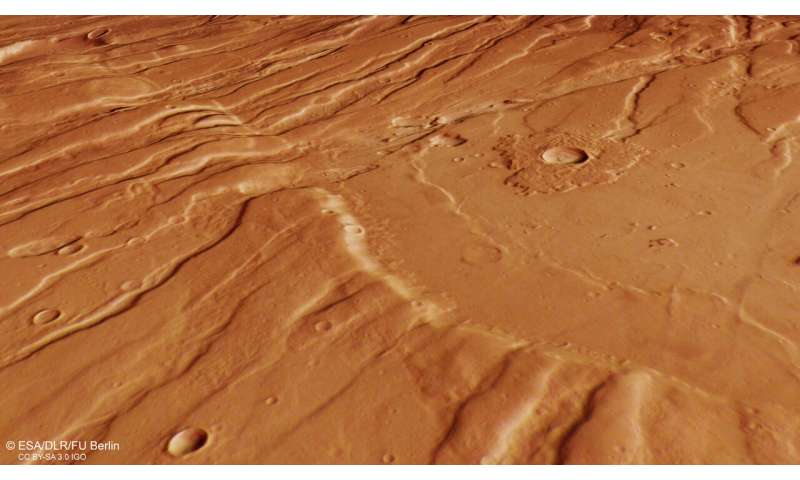
Tempe Fossae is a great example of terrain featuring two key Martian features: grabens and horsts. In a way, these are opposites of one another—grabens are slices of ground that have dropped down between two roughly parallel faults, while horsts are ground that has been uplifted between faults.
At most, the grabens seen here reach a few kilometers wide, a few hundred meters deep, and several hundred kilometers long. Both were created by volcanic and tectonic forces acting across the surface of Mars, which fractured the ground and manipulated it into new configurations. Mars Express has observed these features many times before, in regions including Claritas Fossae, Acheron Fossae, and the nearby Ascuris Planum.
Despite any initial visual confusion, this landscape is a mix of faults, elevated ground, deep valleys, and largely parallel ridges, extending both down into the surface and up above the Martian crust. The crater/dome illusion is actually just a trick of the light caused by our eyes incorrectly interpreting shadows. Comparing this image to the aforementioned image of Ascuris Planum, a similar terrain, highlights this nicely, demonstrating the importance of lighting conditions in photography.
Our Earth-bound eyes are accustomed to seeing images lit from above, but this is not the default orientation for spacecraft, which can gather data at all angles of sunlight.

Mars Express has a peculiar orbit that is not sun-synchronous. Sun-synchronous orbits pass over the same spot on a planetary surface at roughly the same local time of day on every orbit—for instance, Earth orbiters passing over a certain city at around noon every day. Mars Express, however, does not do this, and can therefore gather data at a wide range of local times on Mars. As a result, it experiences a range of different illumination conditions as it observes the Red Planet, and produces a varied array of observations and snapshots of our planetary neighbor.
To the right of the frame (pointing to the planet's north), the surface becomes significantly smoother, with grabens and horsts almost nowhere to be seen. This smoother profile is a result of lava flooding these features before cooling and solidifying, in-filling and resurfacing this part of Mars.
While most of the ridges seen here run parallel to one another from the upper left to lower right, there are also a few scratches cutting across in a perpendicular direction. This is an effect of location, as this patch of terrain is just northeast of the well-known Tharsis province, a past hotspot on Mars for substantial volcanic and tectonic activity.
Tharsis is sizable. The province measures several thousand kilometers across and five kilometers high on average relative to Martian "sea level"—a level that, given the planet's lack of seas, is arbitrarily defined on Mars based on elevation and atmospheric pressure. It hosts the largest volcanoes in the entire solar system, ranging from 15 to over 20 kilometers in height.
-

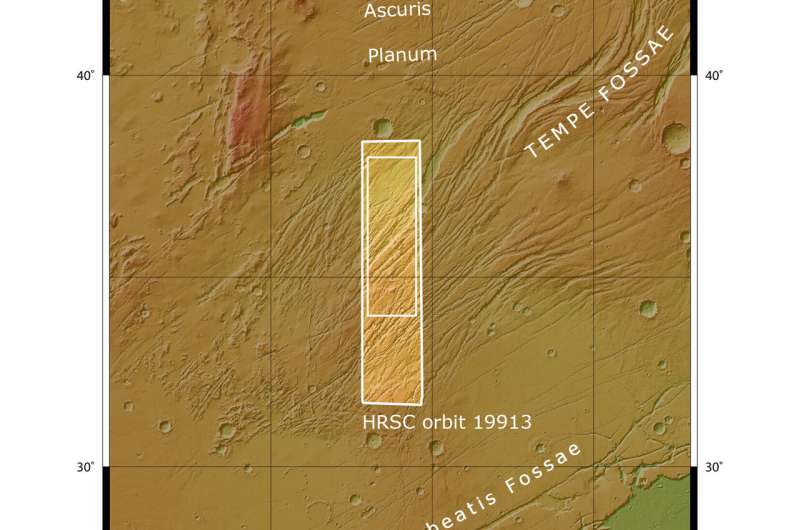
This image shows part of Mars’ surface located northeast of the Tharsis volcanic province in 3D when viewed using red-green or red-blue glasses. This is a portion of Tempe Fossae – a series of tectonic faults that cuts across Tempe Terra in Mars’ northern highlands. This anaglyph was derived from data obtained by the nadir and stereo channels of the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on ESA’s Mars Express during spacecraft orbit 19913. It covers a part of the martian surface centred at 279°E/36°N. North is to the right.. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO -

This image shows a part of Mars’ surface located northeast of the Tharsis volcanic province. This is a portion of Tempe Fossae – a series of tectonic faults that cuts across Tempe Terra in Mars’ northern highlands. It comprises data gathered on 30 September 2019 during orbit 19913. The ground resolution is approximately 15 m/pixel and the images are centred at about 279°E/36°N. This image was created using data from the nadir and colour channels of the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The nadir channel is aligned perpendicular to the surface of Mars, as if looking straight down at the surface. This HRSC stereo imaging was then used to derive a digital elevation model, upon which this oblique view is based. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
As the province grew larger and larger over several hundreds of millions of years, it stretched and stressed the surrounding crust, causing it to fracture and tear in different directions. The perpendicular slices seen in this image are evidence of a change in the direction of stress.
While the formation of Tharsis caused tectonic activity locally, as shown by these slices, it also influenced Mars' crust on a much larger scale and is thought to have had a major influence in forming Valles Marineris, the largest canyon in the solar system. Widespread erosion has occurred in Valles Marineris since its formation, shaping and sculpting the landscape into the canyon system we see today.
Exploring the geology of Mars is a key objective of Mars Express. Launched in 2003, the spacecraft has been orbiting the Red Planet for over a decade and a half; it has since been joined by the ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), which arrived in 2016, while the ExoMars Rosalind Franklin rover and its accompanying surface science platform are scheduled for launch in 2022.
The fleet of spacecraft currently at Mars, operated by several space agencies, are able to image the planet's surface at scales from the global (with a spatial resolution of around ten meters) to the local (spatial resolution of around one meter). This combination allows scientists to characterise geological processes at global, regional, and local scales, enabling them to work towards a fuller understanding of Mars and its intriguing history.
Provided by European Space Agency





















