Mission accomplished for ESA's butane-propelled CubeSat

The cereal-box sized GomX-4B – ESA's biggest small CubeSat yet flown – has completed its mission for the Agency, testing out new miniaturised technologies including: intersatellite link communication with its GomX-4A twin, a hyperspectral imager, star tracker and butane-based propulsion system.
"This multifaceted little mission has performed extremely well in flight," says Roger Walker, overseeing ESA's Technology CubeSats. "What its results demonstrate is that European CubeSats are now ready for operational deployment, as the first generation of CubeSat constellations in low Earth orbit for a variety of applications.
"So our post-flight review has declared ESA's in-orbit demonstration mission a success, but in fact GomX-4B's story is far from over. GomSpace, the manufacturer of the satellite, continues to operate the nanosatellite, while GomSpace's subsidiary in Luxembourg will be in charge of mission exploitation."
Much quicker to build and cheaper to launch than traditional satellites, ESA is making use of CubeSats based on standardised 10 cm boxes for testing new technologies in space.
GomX-4B was ESA's first six-unit CubeSat, double the size of its predecessor GomX-3, built for ESA by GomSpace in Aalborg, Denmark, also the builder of GomX-4A for the Danish Ministry of Defence. The CubeSat pair was launched on 2 February from Jiuquan, China.
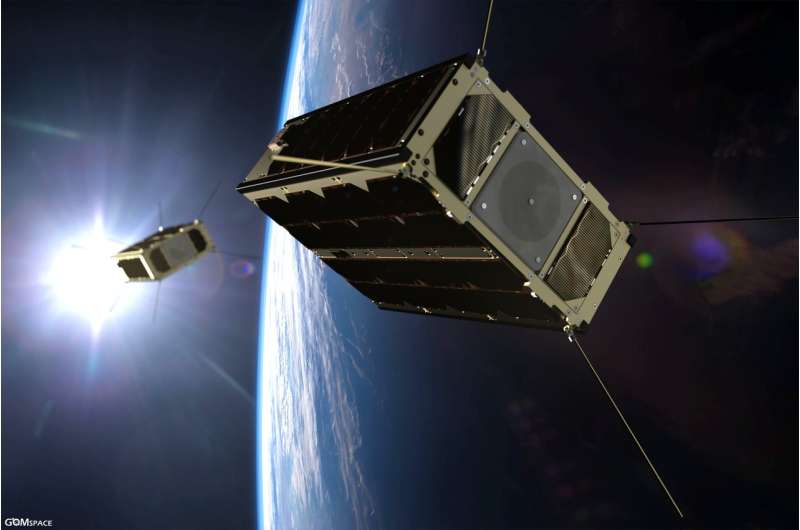

GomX-4B used its butane cold gas propulsion system to manoeuvre away from its twin, flying up to 4500 km away in a fixed geometry – a limit set by Earth's curvature, and representative of planned CubeSat constellation spacing – to test intersatellite radio links allowing the rapid transfer of data from Earth between satellites and back to Earth again.
Supplied by the Swedish branch of GomSpace, the propulsion system allows the CubeSat to adjust its orbital speed in a controlled manner by a total of 10 m/s – a speed equivalent to a kicked football.
"Despite all our orbital manoeuvres, GomX-4B still has a lot of fuel," comments Roger. "Of the original 130 grams of butane, only 13 grams were consumed during the mission."
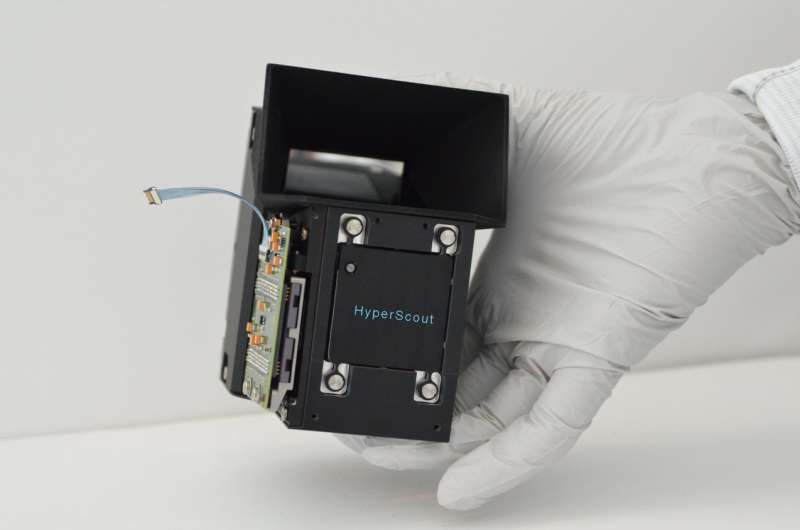
In another first, GomX-4B acquired the first hyperspectral images of Earth from a CubeSat. Cosine Research in the Netherlands and its partners constructed the hand-sized HyperScout imager for ESA. This divides up the light it receives into many narrow, adjacent wavelengths, gathering a wealth of environmental data.
The mission also proved that hyperspectral image processing can be performed aboard, to reduce the amount of data needing to be transmitted down to Earth. High-quality image acquisition requires good pointing accuracy and stability, so GomX-4B also trialled a miniaturised star tracker developed by Dutch CubeSat manufacturer ISIS to orient itself by its surrounding starfield, turning itself using fast-spinning reaction wheels.
A final experimental payload gathered data on how orbital radiation affects computer memories.
The large amount of flight data returned by the mission is being analysed as a source of lessons learnt to guide the development of follow-on CubeSat missions, starting with GomX-5 whose 12-unit design begins next month at GomSpace.
The GomX missions are funded primarily by Denmark in the 'Fly' element of ESA's General Support Technology Programme to develop and prove leading edge space technologies.
ESA has a trio of Technology CubeSats from Belgium planned to fly during the new year: Qarman to gather atmospheric reentry data, Simba to monitor Earth's radiation budget and Picasso to monitor the troposphere and stratosphere.
Provided by European Space Agency