What will happen when our sun dies?
Scientists agree the sun will die in approximately 10 billion years, but they weren't sure what would happen next... until now.
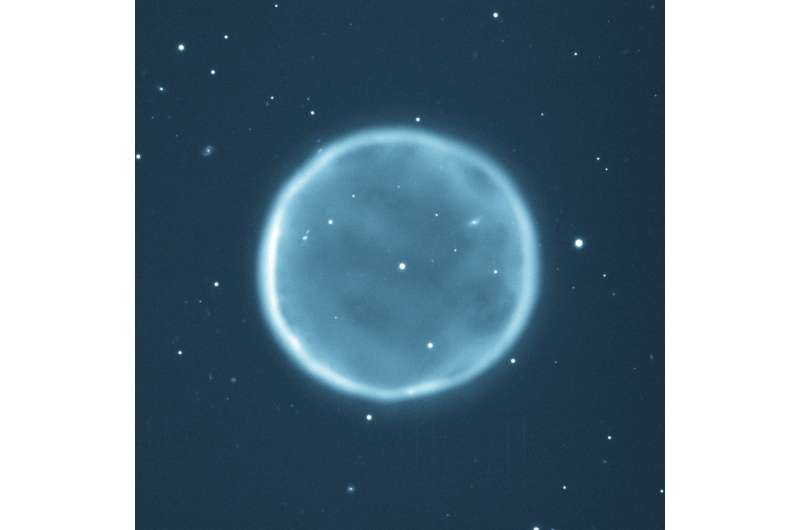
A team of international astronomers, including Professor Albert Zijlstra from the University of Manchester, predict it will turn into a massive ring of luminous, interstellar gas and dust, known as a planetary nebula.
A planetary nebula marks the end of 90% of all stars active lives and traces the star's transition from a red giant to a degenerate white dwarf. But, for years, scientists weren't sure if the sun in our galaxy would follow the same fate: it was thought to have too low mass to create a visible planetary nebula.
To find out the team developed a new stellar, data-model that predicts the lifecycle of stars. The model was used to predict the brightness (or luminosity) of the ejected envelope, for stars of different masses and ages.
The research is being published in Nature Astronomy on Monday 7th May.
Prof Zijslra explains: "When a star dies it ejects a mass of gas and dust—known as its envelope—into space. The envelope can be as much as half the star's mass. This reveals the star's core, which by this point in the star's life is running out of fuel, eventually turning off and before finally dying.
"It is only then the hot core makes the ejected envelope shine brightly for around 10,000 years—a brief period in astronomy. This is what makes the planetary nebula visible. Some are so bright that they can be seen from extremely large distances measuring tens of millions of light years, where the star itself would have been much too faint to see."
The model also solves another problem that has been perplexing astronomers for a quarter of a century.
Approximately 25 years ago astronomers discovered that if you look at planetary nebulae in another galaxy, the brightest ones always have the same brightness. It was found that it was possible to see how far away a galaxy was just from the appearance of its brightest planetary nebulae. In theory it worked in any of type galaxy.
But whilst the data suggested this was correct, the scientific models claimed otherwise. Prof Zijlstra adds: "Old, low mass stars should make much fainter planetary nebulae than young, more massive stars. This has become a source of conflict for the past for 25 years.
"The data said you could get bright planetary nebulae from low mass stars like the sun, the models said that was not possible, anything less than about twice the mass of the sun would give a planetary nebula too faint to see."
The new models show that after the ejection of the envelope, the stars heat up three times faster than found in older models. This makes it much easier for a low mass star, such as the sun, to form a bright planetary nebula. The team found that in the new models, the sun is almost exactly the lowest mass star that still produces a visible, though faint, planetary nebula. Stars even a few per cent smaller do not.
Professor Zijlstra added: "We found that stars with mass less than 1.1 times the mass of the sun produce fainter nebula, and stars more massive than 3 solar masses brighter nebulae, but for the rest the predicted brightness is very close to what had been observed. Problem solved, after 25 years!
"This is a nice result. Not only do we now have a way to measure the presence of stars of ages a few billion years in distant galaxies, which is a range that is remarkably difficult to measure, we even have found out what the sun will do when it dies!"
More information: The mysterious age invariance of the planetary nebula luminosity function bright cut-off, Nature Astronomy (2018). nature.com/articles/doi:10.1038/s41550-018-0453-9
Journal information: Nature Astronomy
Provided by University of Manchester



















