Discovery of long chain non-coding RNAs activating sex determination genes
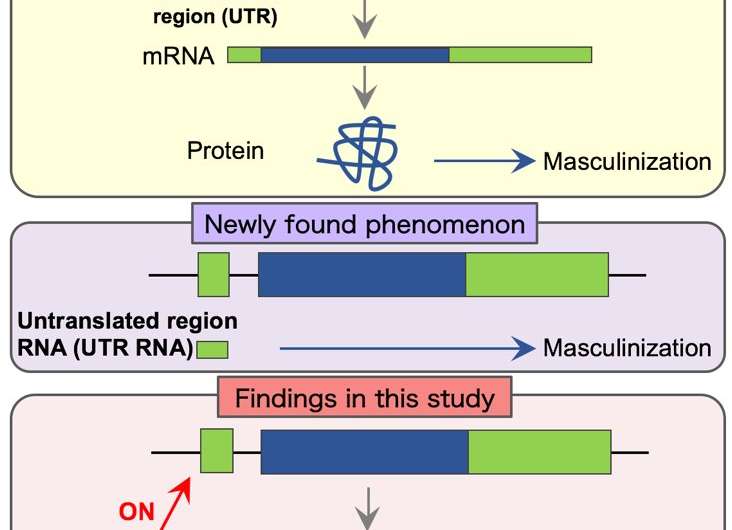
The messenger RNA (mRNA) that conveys genetic information has a region that can be translated into protein (translated region). A noncoding area (ncRNA), which has no translated region (TR), has not been thought to be important; however, recent studies revealed that ncRNAs are transcribed from thousands of loci in genomes.
Of the ncRNA, the number of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), RNAs with greater than 200 bases, is said to be over 20,000 in human. However, commonality and diversity in the mechanism of IncRNAs, as well as conservation of their function among living organisms, have not been clarified.
Researchers led by Hajime Watanabe at Osaka University discovered lncRNAs to activate the male-determining gene doublesex1 (Dsx1) necessary for sex determination in the crustacean Daphnia magna. Their research results were published in Current Biology.
The researchers had found that proteins produced from the TR of the Dsx1 gene induced masculinization in the crustacean Daphnia magna. (Figure 1 top)
"In this study, we discovered an interesting phenomenon: masculinization is also caused by the untranslated regions (UTRs) on a strand of mRNA. The UTRs do not form the protein-coding region of the Dsx1 gene," said lead author Yasuhiko Kato. (Figure 1 center, Figure 2)
Proposing the hypothesis that a sequence in the UTR of the Dsx1 gene also serves as part of lncRNAs and naming the RNA doublesex1 alpha promoter-associated long RNA (DAPALR), the researchers examined the synthesis and function of the RNA. As a result, they found that the UTR overlapping with part of DAPALR-activated Dsx1, by which Dsx1 proteins were produced, causing masculinization. (Figure 1 bottom, Figure 3)
Their achievements will contribute to the understanding of the functional mechanism of lncRNAs as well as diversity in and evolution of the sex-determining mechanism.
-
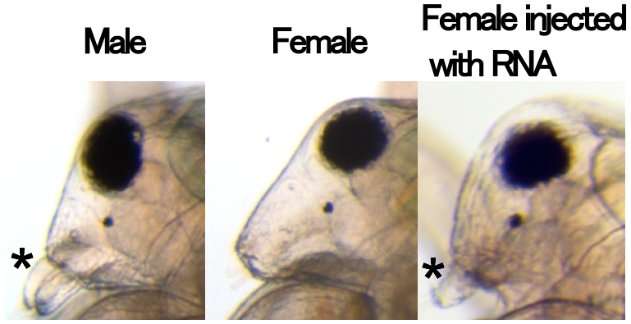
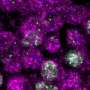
Figure 2. Masculinization in females injected with RNA that codes for the UTR of Dsx1. The asterisks indicate elongation of the first antennae. Credit: Osaka University -
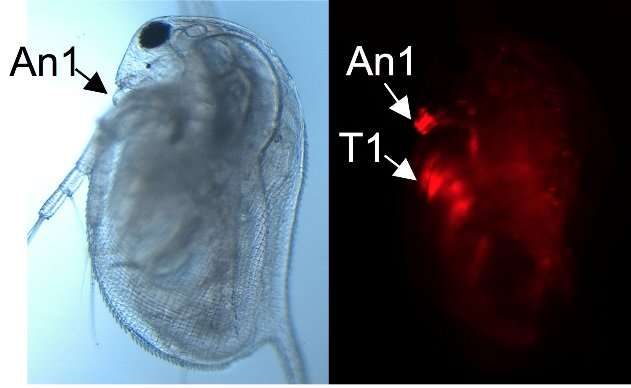
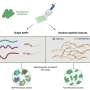
Figure 3. Lateral view of a female juvenile overexpressing DAPALR. A dsx1-reporter Daphnia magna that expresses mCherry under control of the Dsx1 promoter/enhancer was used. Left: Elongation of the first antennae (An1) in a female overexpressing DAPALR. Right: mCherry expression in An1 and the first thoracic appendages (T1) in the same individual. Credit: Osaka University
More information: Yasuhiko Kato et al. A 5′ UTR-Overlapping LncRNA Activates the Male-Determining Gene doublesex1 in the Crustacean Daphnia magna, Current Biology (2018). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.04.029
Journal information: Current Biology
Provided by Osaka University