3-D images of cancer cells in the body: Physicists present new method
Medical physicists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have developed a new method that can generate detailed three-dimensional images of the body's interior. These can be used to more closely investigate the development of cancer cells. The research group published its findings in Communication Physics.
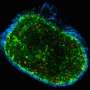
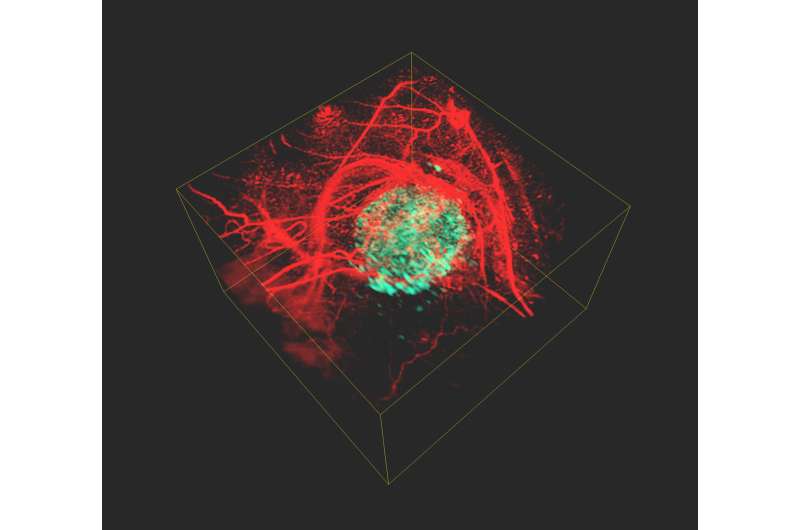
Clinicians and scientists seek to better understand cancer cells and their properties in order to provide targeted cancer treatment. Individual cancer cells are often examined in test tubes before the findings are tested in living organisms. "Our aim is to visualise cancer cells inside the living body to find out how they function, how they spread and how they react to new therapies," says medical physicist Professor Jan Laufer from MLU. He specialises in the field of photoacoustic imaging, a process that uses ultrasound waves generated by laser beams to produce high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the body's interior.
"The problem is that tumour cells are transparent. This makes it difficult to use optical methods to examine tumours in the body," explains Laufer, whose research group has developed a new method to solve this problem. First, the scientists introduce a specific gene into the genome of the cancer cells.
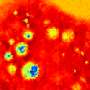
"Once inside the cells, the gene produces a phytochrome protein, which originates from plants and bacteria. There it serves as a light sensor," Laufer says. In the next step, the researchers illuminate the tissue with short pulses of light at two different wavelengths using a laser. Inside the body, the light pulses are absorbed and converted into ultrasonic waves. These waves can then be measured outside the organism, and two images of the body's interior can be reconstructed based on this data.
"The special feature of phytochrome proteins is that they alter their structure and thus also their absorption properties, depending on the wavelength of the laser beams. This results in changes to the amplitude of the ultrasound waves that are generated in the tumour cells. None of the other tissue components, for example, blood vessels, have this property—their signal remains constant," Laufer says. By calculating the difference between the two images, a high-resolution, three-dimensional image of the tumour cells is created, which is free of the otherwise overwhelming background contrast.
The development of Halle's medical physicists can be applied to a wide range of applications in the preclinical research and the life sciences. In addition to cancer research, the method can be used to observe cellular and genetic processes in living organisms.
More information: Julia Märk et al, Dual-wavelength 3D photoacoustic imaging of mammalian cells using a photoswitchable phytochrome reporter protein, Communications Physics (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s42005-017-0003-2
Provided by Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg