Pigments in oil paintings linked to artwork degradation

Experts have long known that as oil paintings age, soaps can form within the paint, degrading the appearance of the artworks. The process significantly complicates the preservation of oil paintings—and cultural manifestations, which the paintings themselves help to preserve.
"These soaps may form protrusions that grow within the paint and break up through the surface, creating a bumpy texture," said Silvia Centeno, a member of the Department of Scientific Research at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art (The Met). "In other cases, the soaps can increase the transparency of the paint, or form a disfiguring, white crust on the painting."
Scientists do not understand why the soaps take on different manifestations, and for many years, the underlying mechanisms of how the soaps form remained a mystery.
"The Met, alongside our colleagues from other institutions, is trying to figure out why the process takes place, what triggers it, and if there's a way we can prevent it," Centeno said.
X-rays reveal new clues
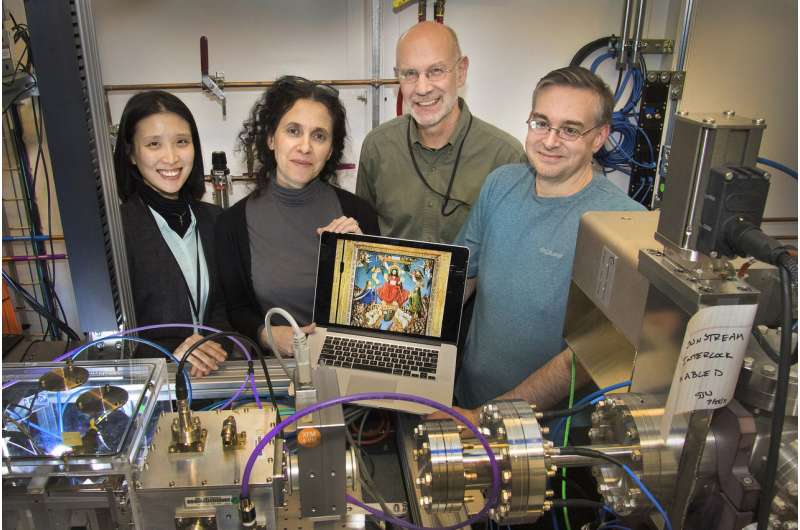
Recently, a scientific collaboration led by researchers at The Met, the University of Delaware, and the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has helped to answer one of these questions. By analyzing a microscopic sample from The Crucifixion, a 15th century oil painting by Jan Van Eyck, the research team was able to determine which components in the paint were responsible for forming soaps. Their findings were published in Scientific Reports.
"When we study paintings at the museum, we try to use noninvasive techniques—methods that do not induce permanent changes in the artwork," Centeno said. "However, in some cases, we need to remove a very small sample for analysis. We will take it from areas where there is already a crack or a loss in the artwork. All the samples are archived so we can go back and reuse them, and in this case, the sample we studied had already been removed from the painting for another study when we realized it was a good example of soap formation."
In order to study the tiny chemical features the sample, the scientists needed the advanced capabilities of the x-ray microscope at beamline 5-ID at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II)—a DOE Office of Science user facility at Brookhaven Lab. This beamline has the unique ability to image the chemical makeup of complex structures, making it the perfect tool for studying small samples from works of art.
"Because these samples are so small, we needed beamline 5-ID's sub-micron spatial resolution, and the expertise of the beamline staff," Centeno said.
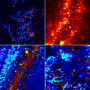
Using a research technique called x-ray fluorescence microscopy, the scientists directed NSLS-II's ultra-bright x-rays at the painting sample while moving the sample horizontally and vertically. This enabled them to generate maps that show how different elements are distributed in the sample, and determine how these elements had moved within the paint due to the deterioration. Additionally, using a technique called x-ray absorption spectroscopy, the scientists identified the presence of chemical compounds that were the products of deterioration reactions within the sample.
"It had been proposed that impurities in one of the pigments that is typically involved in soap formation, called lead tin yellow type I, were responsible for soap formation, and we found this is not the case," Centeno said. "While the impurities may be reacting, it is the main components of this pigment—the pigment that gives the paint color—that react during soap formation. The heavy metals in pigments, such as lead tin yellow and others, react with fatty acids in the oil binding medium to form soaps. This causes the paint to change its color and aspect, and what was intended by the artist."
This finding is an important step toward fully understanding soap formation, and developing a method to preserve the color and texture of oil paintings.
"It was a privilege to be part of this collaboration," said Karen Chen-Wiegart, an Assistant Professor at Stony Brook University with a joint appointment at NSLS-II. "It is a rare opportunity to be able to work with a sample that carries so much history. When our staff saw that we were scanning this art in real-time, everyone got so excited because they saw that their tools could be used to study something they never thought was possible. It was exciting at multiple levels for all of us here at NSLS-II."
While the current study focused on one type of pigment, the collaboration intends to study how soap formation varies among different pigments, as well as the effects of temperature, humidity, and the paint's porosity. They also hope to use a wider range of synchrotron techniques at NSLS-II to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the deterioration mechanism.
More information: Yu-chen Karen Chen-Wiegart et al. Elemental and Molecular Segregation in Oil Paintings due to Lead Soap Degradation, Scientific Reports (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11525-1
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Brookhaven National Laboratory