The oldest plesiosaur was a strong swimmer

Plesiosaurs were especially effective swimmers. These long extinct "paddle saurians" propelled themselves through the oceans by employing "underwater flight"—similar to sea turtles and penguins. Paleontologist from the University of Bonn, Germany, together with colleagues from Japan and France, now describe the oldest plesiosaur in the journal Science Advances. The fossil comes from the earliest part of the Triassic period and is about 201 million years old.
Instead of laboriously pushing the water out of the way with their paddles, plesiosaurs glided with limbs modified as underwater wings. They had small heads and long, streamlined necks. Their stout bodies had strong muscles to keep those wings in motion. Compared to other marine reptiles, the tail was short, because it was only used for steering. This evolutionary design was very successful, but curiously, it did not evolve again after the extinction of the plesiosaurs, according to paleontologist Prof. Martin Sander from the Steinmann Institute of Geology, Mineralogy, and Paleontology of the University of Bonn.
The long-extinct paddle saurians could easily have held their own against today's water animals. Whereas sea turtles mainly use their strong forelimbs for propulsion, the plesiosaurs moved all four limbs together, resulting in powerful thrust. These ancient animals did not have a shell like turtles, however. Plesiosaurs fed on fish. Numerous fossils document a global distribution of the group during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
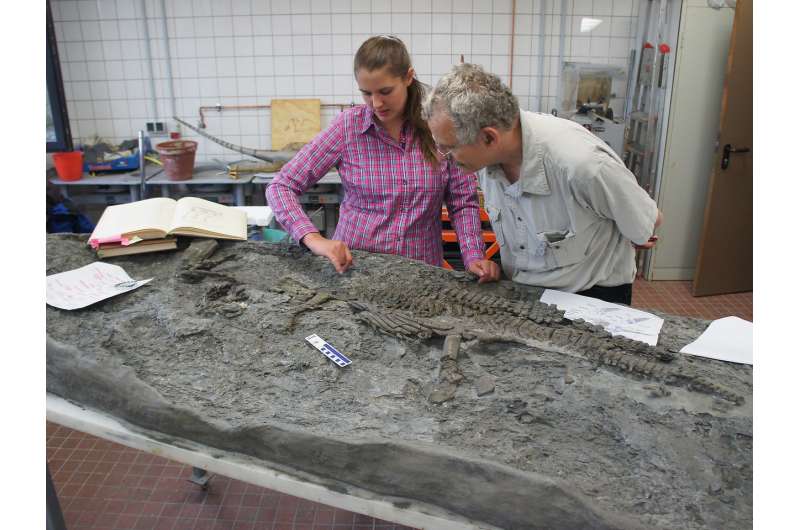
The private collector Michael Mertens discovered a truly exceptional specimen during quarrying operations in a clay pit in Westphalia, Germany, in 2013. The subsequent evaluation by the LWL-Museum für Naturkunde in Münster, Germany, revealed that the find represents a marine reptile from the Triassic, the period that predates the Jurassic. This news reached Prof. Sander of the University of Bonn while on sabbatical in Los Angeles. "I could not believe that there was a plesiosaur from the Triassic, given that these animals had been studied by paleontologist for nearly 300 years, and never was there one older than Jurassic," said Sander.
He also notes that only through the timely and efficient cooperation between the private collector, the natural heritage protection agency, the Münster museum, and the scientists, the unique find could be described and published. The detailed research by Ph.D. student Tanja Wintrich of the Steinmann Institute of the University of Bonn revealed that the find represents the oldest plesiosaur, at an age of about 201 million years, which makes it the only plesiosaur skeleton from the Triassic period.
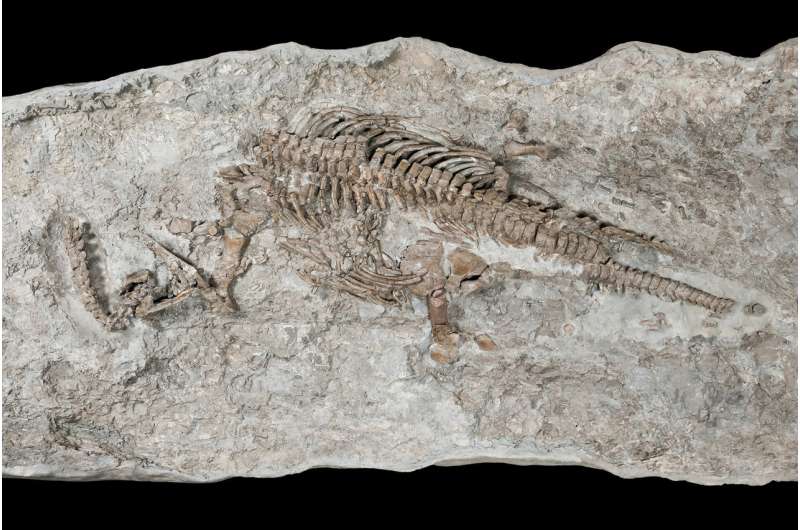

The reconstructed length of the skeleton is 237 cm (7' 7") (part of the neck was lost to quarrying). "We are looking at a relatively small plesiosaur," says Wintrich. The scientists bestowed the name Rhaeticosaurus mertensi on the unique fossil. The first part of the name refers to its geologic age (Rhaetian) and the second part honors the discoverer. Together with scientists from Osaka Natural History Museum, the University of Osaka, the University of Tokyo and the Paris Natural History Museum, the team from Bonn studied a bone sample. First, they examined the interior of the bone using computed tomography. Then they cut thin sections for microscopic study from especially promising parts of the bone.
Based on the growth marks in the bones, the researchers recognized that Rhaeticosaurus was a fast-growing youngster. They compared the thin sections with those from young plesiosaurs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous. "Plesiosaurs apparently grew extremely fast before reaching sexual maturity," says Sander. The paleontologists interprets this as a clear indication that plesiosaurs were warm-blooded. Since plesiosaurs spread quickly all over the world, "they must have been able to regulate their body temperature to be able to invade cooler parts of the ocean," says the paleontologist. Because of their warm-bloodedness and their efficient locomotion, plesiosaurs were extremely successful and widespread—until they disappeared from the face of the earth. Sander says, "At the end of the Cretaceous, a meteorite impact together with volcanic eruptions lead to an ecosystem collapse, of which plesiosaurs were prominent victims."
More information: Tanja Wintrich, Shoji Hayashi, Alexandra Houssaye, Yasuhisa Nakajima, P. Martin Sander: A Triassic plesiosaurian skeleton and bone histology inform on evolution of a unique body plan, Science Advances, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1701144 , advances.sciencemag.org/content/3/12/e1701144
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by University of Bonn