Researchers gain control over single atoms
University of Otago physicists have found a way to control individual atoms, making them appear wherever they want them to.
The accomplishment, by a team of six from Otago's Department of Physics, follows an international breakthrough in 2010 when they isolated and captured a neutral rubidium-85 atom, and then photographed it for the first time.
Lead Otago researcher Dr Mikkel Andersen says their results may be beneficial in the future development of a wide range of technologies, including incredibly fast quantum computers for calculations of extreme complexity.
"Time will tell what the applications will be. It is likely the main applications will be in technologies we have not yet thought about."
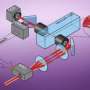
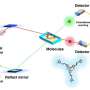
To achieve their successes, the team uses seven lasers, with components from compact disc players, and precision mirrors.
They work in an air-conditioned laboratory from which as many kinds of "noise" – electromagnetic, sound, temperature contrasts – that can affect the equipment and results have been minimised or eliminated using "Kiwi ingenuity".
Dr Andersen says laser light is the key.
"We cool the atoms, hold them, change how they affect each other and make them visible by shining laser light, with different frequency and intensity, on them. We make repeated use of the phenomenal degree of control one can have over the frequency of laser light, which is a truly astounding feature of lasers.
"The 'Kiwi ingenuity' is how we circumvented the fact that we do not have a low-noise laboratory as would usually be considered a necessity for experiments like ours. Naturally, finding out how to do things that have never been done before involves lots of hard work."
The tables on which the experiment has been built float on air, one way of keeping down the "noise", he says.
Dropping the temperature of the atom to almost absolute zero (minus 273 degrees Celsius), eliminates its "random wobbling", allowing it to reach a quantum state with high purity.
"This represents the ultimate control over individual atoms.
"We are pushing the boundaries for the level of control that scientists can have over microscopic systems. Technical revolutions our society has undergone in past decades largely, if not entirely, originate from being able to control systems at a smaller and smaller scale.
"This has been a long journey. This is what we have been trying to get to for 10 years," Dr Andersen says.
The Marsden Fund supported the research with $717,391 over three years. The team's findings are about to appear in Physical Review A, Rapid Communications.
The next steps are investigations of how two atoms being brought together can exchange properties, and building molecules in particular quantum states from individual atoms.
Provided by University of Otago