Vinegar could potentially help treat ulcerative colitis
Vinegar is the perfect ingredient for making tangy sauces and dressings. Now, researchers report in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry that the popular liquid could also help fight ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease that research suggests is related to the gut microbiome. They found that vinegar suppressed inflammation-inducing proteins while improving the gut's bacterial makeup in mice.
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition that affects millions of people around the world. Although its cause isn't completely understood, research suggests that bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract play an important part. People with the condition experience repeated inflammation of the large intestine's lining, which can cause ulcers, abdominal pain, diarrhea and other symptoms. At least one recent study suggested that vinegar, which has been used in traditional medicine for centuries, might be effective against ulcerative colitis. Lu Yu, Bo Liu and colleagues wanted to further investigate this possibility.
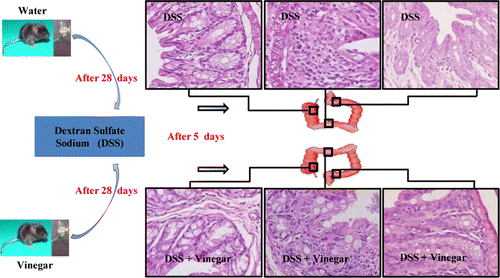
The researchers tested vinegar and its main ingredient, acetic acid, in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. Giving the mice either substance by adding it in small amounts to their drinking water significantly reduced symptoms of the condition. An analysis of mouse stool samples showed that treated animals had higher levels of bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria. Other studies have found these bacteria to be beneficial to mice with colitis-like symptoms. Treatment also lowered the levels of proteins that induce potentially damaging inflammation in the gut. The researchers say further work would be needed to determine vinegar's effects on ulcerative colitis in humans.
More information: Fengge Shen et al. Vinegar Treatment Prevents the Development of Murine Experimental Colitis via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2016). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05415
Abstract
This study investigated the preventive effects of vinegar and acetic acid (the active component of vinegar) on ulcerative colitis (UC) in mice. Vinegar (5% v/v) or acetic acid (0.3% w/v) treatment significantly reduced the disease activity index and histopathological scores, attenuated body weight loss, and shortened the colon length in a murine experimental colitis model induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). Further mechanistic analysis showed that vinegar inhibited inflammation through suppressing Th1 and Th17 responses, the NLRP3 inflammasome, and MAPK signaling activation. Vinegar also inhibited endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis in the colitis mouse model. Surprisingly, pretreatment with vinegar for 28 days before DSS induction increased levels of the commensal lactic acid-producing or acetic acid-producing bacteria, including Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria, and Enterococcus faecalis, whereas decreased Escherichia coli levels were found in the feces of mice. These results suggest that vinegar supplementation might provide a new dietary strategy for the prevention of UC.
Journal information: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Provided by American Chemical Society